Glossary
Creep (Rheology)
CreepCreep describes a time and temperature dependent plastic deformation under a constant force. When a constant force is applied to a rubber compound, the initial deformation obtained due to the application of the force is not fixed. The deformation will increase with time.Creep is one of the earliest “controlled StressStress is defined as a level of force applied on a sample with a well-defined cross section. (Stress = force/area). Samples having a circular or rectangular cross section can be compressed or stretched. Elastic materials like rubber can be stretched up to 5 to 10 times their original length.stress” rheometer tests that quite literally “creeps” the material, i.e. we measure over a relatively prolonged period the small movement (the CreepCreep describes a time and temperature dependent plastic deformation under a constant force. When a constant force is applied to a rubber compound, the initial deformation obtained due to the application of the force is not fixed. The deformation will increase with time.creep defined as CreepCreep describes a time and temperature dependent plastic deformation under a constant force. When a constant force is applied to a rubber compound, the initial deformation obtained due to the application of the force is not fixed. The deformation will increase with time.creep compliance, J) of the sample by applying a small constant StressStress is defined as a level of force applied on a sample with a well-defined cross section. (Stress = force/area). Samples having a circular or rectangular cross section can be compressed or stretched. Elastic materials like rubber can be stretched up to 5 to 10 times their original length.stress.
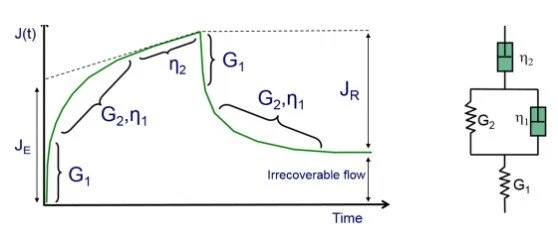
The benefit of this type of measurement is that even with small applied StressStress is defined as a level of force applied on a sample with a well-defined cross section. (Stress = force/area). Samples having a circular or rectangular cross section can be compressed or stretched. Elastic materials like rubber can be stretched up to 5 to 10 times their original length.stress, the typically small resultant deformation (J) builds up to be significant over time.
From a rheological point of view is that this also starts to indicate the “viscoelastic” properties of the material as they are resolved with time into the following regions:
- G1 which is the initial fast “elastic” response where the elastic structure stretches
- G2/η1 is now the “viscoelastic” response which still has some rapid elastic StressStress is defined as a level of force applied on a sample with a well-defined cross section. (Stress = force/area). Samples having a circular or rectangular cross section can be compressed or stretched. Elastic materials like rubber can be stretched up to 5 to 10 times their original length.stress, but slowed down a little with the slower viscous response
- η2 is now the “viscous” region, where all the elastic structure (JE) has been stretched and we are left with pure viscous flow
As such, early generation rotational rheometers often used CreepCreep describes a time and temperature dependent plastic deformation under a constant force. When a constant force is applied to a rubber compound, the initial deformation obtained due to the application of the force is not fixed. The deformation will increase with time.creep testing as a form of “high resolution” viscosity measurement to ensure that each data point of a flow curve was at “steady state”, i.e. pure viscous flow.
However, as next generation rheometers such as the Kinexus by NETZSCH has “live data” for each data point in a flow curve, steady state can also be checked without using a specific CreepCreep describes a time and temperature dependent plastic deformation under a constant force. When a constant force is applied to a rubber compound, the initial deformation obtained due to the application of the force is not fixed. The deformation will increase with time.creep test.
CreepCreep describes a time and temperature dependent plastic deformation under a constant force. When a constant force is applied to a rubber compound, the initial deformation obtained due to the application of the force is not fixed. The deformation will increase with time.Creep therefore now tends to be used for more specialist testing, such as looking at the prolonged effects of small applied stresses (such as gravity) on a material, or mimicking applied processes such as the Multiple Stress Creep Recovery (MSCR)The method is designed to identify the presence of elastic response in an asphalt binder. MSCR (Multiple StressStress is defined as a level of force applied on a sample with a well-defined cross section. (Stress = force/area). Samples having a circular or rectangular cross section can be compressed or stretched. Elastic materials like rubber can be stretched up to 5 to 10 times their original length.Stress CreepCreep describes a time and temperature dependent plastic deformation under a constant force. When a constant force is applied to a rubber compound, the initial deformation obtained due to the application of the force is not fixed. The deformation will increase with time.Creep and Recovery) test for bitumen/asphalt samples.
The Recovery part of the CreepCreep describes a time and temperature dependent plastic deformation under a constant force. When a constant force is applied to a rubber compound, the initial deformation obtained due to the application of the force is not fixed. The deformation will increase with time.Creep test is a common extension to validate the CreepCreep describes a time and temperature dependent plastic deformation under a constant force. When a constant force is applied to a rubber compound, the initial deformation obtained due to the application of the force is not fixed. The deformation will increase with time.creep results. Now the rheometer turns off the small applied StressStress is defined as a level of force applied on a sample with a well-defined cross section. (Stress = force/area). Samples having a circular or rectangular cross section can be compressed or stretched. Elastic materials like rubber can be stretched up to 5 to 10 times their original length.stress, to literally measure the recovery with time, where the CreepCreep describes a time and temperature dependent plastic deformation under a constant force. When a constant force is applied to a rubber compound, the initial deformation obtained due to the application of the force is not fixed. The deformation will increase with time.creep elastic compliance (JE) should be the same as the recovery elastic compliance (JR). Again the “elastic” response is the fastest (G1), followed by the “viscoelastic” response (G2/η1). As viscous flow does not have any recovery we have the irrecoverable flow region which is the same as how far the sample viscous flows.

