Glossary
Yield Stress
Yield StressStress is defined as a level of force applied on a sample with a well-defined cross section. (Stress = force/area). Samples having a circular or rectangular cross section can be compressed or stretched. Elastic materials like rubber can be stretched up to 5 to 10 times their original length.stress is defined as the StressStress is defined as a level of force applied on a sample with a well-defined cross section. (Stress = force/area). Samples having a circular or rectangular cross section can be compressed or stretched. Elastic materials like rubber can be stretched up to 5 to 10 times their original length.stress below which no flow occurs; literally behaves like a weak solid at rest and a liquid when yielded.
Many Shear ThinningThe most common type of non-Newtonian behavior is shear thinning or pseudoplastic flow, where the fluid viscosity decreases with increasing shear.shear-thinning fluids can be considered to possess both liquid and solid like properties. At rest or near rest conditions, these fluids are able to form intermolecular or inter-particle networks as a result of polymer entanglements, particle association, or some other associated interaction. The presence of this network structure gives the material predominantly solid-like characteristics associated with elasticity. The strength of which is directly related to the inter-molecular or inter-particle forces (binding force) holding the network together, and hence its yield StressStress is defined as a level of force applied on a sample with a well-defined cross section. (Stress = force/area). Samples having a circular or rectangular cross section can be compressed or stretched. Elastic materials like rubber can be stretched up to 5 to 10 times their original length.stress.
If an external StressStress is defined as a level of force applied on a sample with a well-defined cross section. (Stress = force/area). Samples having a circular or rectangular cross section can be compressed or stretched. Elastic materials like rubber can be stretched up to 5 to 10 times their original length.stress is applied which is less than the yield StressStress is defined as a level of force applied on a sample with a well-defined cross section. (Stress = force/area). Samples having a circular or rectangular cross section can be compressed or stretched. Elastic materials like rubber can be stretched up to 5 to 10 times their original length.stress, the material will deform elastically. However, when the external StressStress is defined as a level of force applied on a sample with a well-defined cross section. (Stress = force/area). Samples having a circular or rectangular cross section can be compressed or stretched. Elastic materials like rubber can be stretched up to 5 to 10 times their original length.stress exceeds the yield StressStress is defined as a level of force applied on a sample with a well-defined cross section. (Stress = force/area). Samples having a circular or rectangular cross section can be compressed or stretched. Elastic materials like rubber can be stretched up to 5 to 10 times their original length.stress, the network structure will collapse and the material will begin to flow as if it is a liquid.
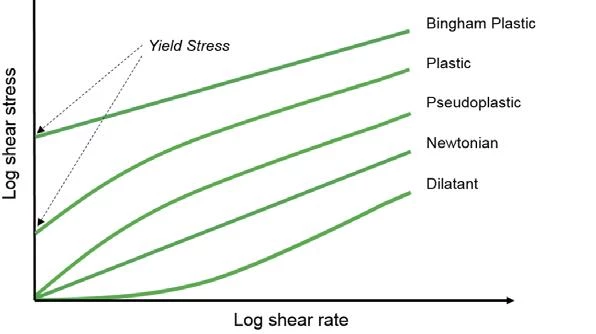
Modern rheometers have many advantages over on early viscometer type indirect (extrapolated) yield StressStress is defined as a level of force applied on a sample with a well-defined cross section. (Stress = force/area). Samples having a circular or rectangular cross section can be compressed or stretched. Elastic materials like rubber can be stretched up to 5 to 10 times their original length.stress measurements. The Kinexus rotational rheometer by NETZSCH gives several different methods to quantify yield StressStress is defined as a level of force applied on a sample with a well-defined cross section. (Stress = force/area). Samples having a circular or rectangular cross section can be compressed or stretched. Elastic materials like rubber can be stretched up to 5 to 10 times their original length.stress dependent on the material type. Usually a direct yield StressStress is defined as a level of force applied on a sample with a well-defined cross section. (Stress = force/area). Samples having a circular or rectangular cross section can be compressed or stretched. Elastic materials like rubber can be stretched up to 5 to 10 times their original length.stress measurement works well by increasing the stress applied to the sample directly, until the material flows.

