Glossary
Burgers Model
The Burgers Model is a general model of a viscoelastic material, commonly used to describe a classic CreepCreep describes a time and temperature dependent plastic deformation under a constant force. When a constant force is applied to a rubber compound, the initial deformation obtained due to the application of the force is not fixed. The deformation will increase with time.creep recovery measurement (see CreepCreep describes a time and temperature dependent plastic deformation under a constant force. When a constant force is applied to a rubber compound, the initial deformation obtained due to the application of the force is not fixed. The deformation will increase with time.Creep).
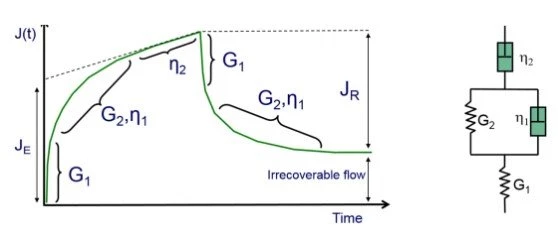
The model is a combination of spring and dashpots, arranged as combination of separate component in series and in parallel.
- Springs - indicate an elastic response. When “pulled” under an applied StressStress is defined as a level of force applied on a sample with a well-defined cross section. (Stress = force/area). Samples having a circular or rectangular cross section can be compressed or stretched. Elastic materials like rubber can be stretched up to 5 to 10 times their original length.stress load will instantly stretch to a defined length (StrainStrain describes a deformation of a material, which is loaded mechanically by an external force or stress. Rubber compounds show creep properties, if a static load is applied.strain), and recover completely to the initial state when the load is removed. (Should the applied StressStress is defined as a level of force applied on a sample with a well-defined cross section. (Stress = force/area). Samples having a circular or rectangular cross section can be compressed or stretched. Elastic materials like rubber can be stretched up to 5 to 10 times their original length.stress be larger than what the spring can absorb, permanent/non-recoverable deformation will occur, see “yield StressStress is defined as a level of force applied on a sample with a well-defined cross section. (Stress = force/area). Samples having a circular or rectangular cross section can be compressed or stretched. Elastic materials like rubber can be stretched up to 5 to 10 times their original length.stress”.)
- Dashpots – indicate a viscous response. When “pulled” under an applied StressStress is defined as a level of force applied on a sample with a well-defined cross section. (Stress = force/area). Samples having a circular or rectangular cross section can be compressed or stretched. Elastic materials like rubber can be stretched up to 5 to 10 times their original length.stress load will move over time (with a speed dependent the viscosity), and continue to move until the load is removed. There is no recovery when the load is removed and stays permanent deformed.
So, in the Burgers models G1 and η2 are independent in series and model the separate elastic and viscous components of a material.
G2 and η1 are in parallel which mimics the viscoelastic component of a sample where the immediate spring/elastic response is “dampened” (slowed) by the dashpot/viscous component when a load is applied.
With the StressStress is defined as a level of force applied on a sample with a well-defined cross section. (Stress = force/area). Samples having a circular or rectangular cross section can be compressed or stretched. Elastic materials like rubber can be stretched up to 5 to 10 times their original length.stress load removed, G2 recovers, but again is dampened by η1, but will recover completely as long as the applied StressStress is defined as a level of force applied on a sample with a well-defined cross section. (Stress = force/area). Samples having a circular or rectangular cross section can be compressed or stretched. Elastic materials like rubber can be stretched up to 5 to 10 times their original length.stress is linear, i.e. within the “Linear Viscoelastic Region (LVER)In the LVER, applied stresses are insufficient to cause structural breakdown (yielding) of the structure and hence important micro-structural properties are being measured.linear viscoelastic region”.
