Glossary
Debinding
Debinding is one of the main production steps in the ceramic and powder-metallurgical industries. It refers to the thermal or catalytic removal of additives used in steps prior to production such as casting.
The debinding process for ceramic materials commonly takes place in oxygen-containing atmospheres and results in complete combustion of the organic components. In contrast, in powder-metallurgy often inert atmosphere is required for the debinding process.
Debinding processes can be investigated by means of Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) and Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC).
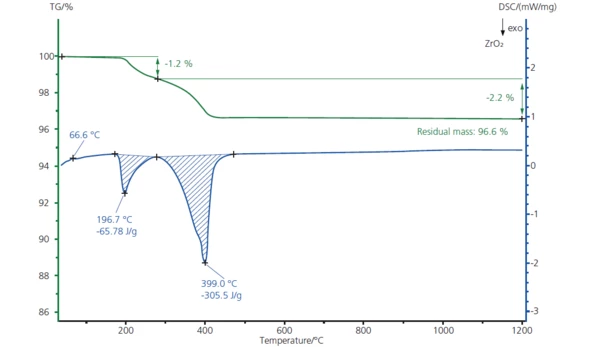
The figure below shows an STA measurement of the debinding process for zirconium dioxide (26.2 mg). The sample was treated in an oxidative atmosphere, resulting in the detection of two mass-loss steps in the temperature range up to 500°C. The mass-loss steps were accompanied by ExothermicA sample transition or a reaction is exothermic if heat is generated.exothermic effects which indicate the oxidative burn-up of the binder components.