Glossaire
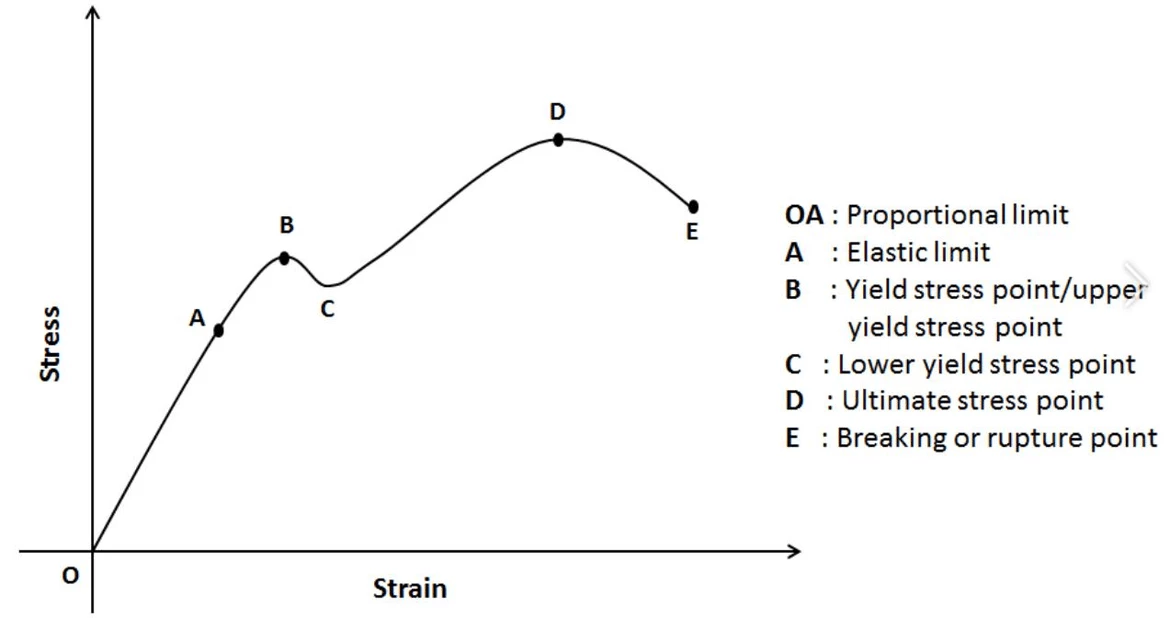
Stress-Strain Behavior
The figure shows a typical ContrainteLa Contrainte est définie par un niveau de force appliquée sur un échantillon d’une section bien définie. (Contrainte = force/surface). Les échantillons qui possèdent une section rectangulaire ou circulaire peuvent être comprimés ou étirés. Les matériaux élastiques comme les élastomères peuvent être étirés jusqu’à 5 à 10 fois leur longueur initiale.stress-strain plot of an elastomer.
The most noticeable feature is its non-linearity, which takes place from A to E. Only in the range from 0 to A (normally the corresponding strain reaching the limit of linearity is not larger than 1 %), the stress/strain ratio results in a constant number: the Elastic modulusThe complex modulus (elastic component), storage modulus, or G’, is the “real” part of the samples the overall complex modulus. This elastic component indicates the solid like, or in phase, response of the sample being measurement. Elastic modulus.
This behavior can be measured with the DMA Eplexor®®.