Glossario
Creep Compliance (J)
La Creep Compliance (J, o funzione di creep) è il rapporto, riportato in Pa-1, tra la deformazione (shear StrainStrain describes a deformation of a material, which is loaded mechanically by an external force or stress. Rubber compounds show creep properties, if a static load is applied.strain) e lo sforzo (shear StressStress is defined as a level of force applied on a sample with a well-defined cross section. (Stress = force/area). Samples having a circular or rectangular cross section can be compressed or stretched. Elastic materials like rubber can be stretched up to 5 to 10 times their original length.stress), come misura della deformazione istantanea e continua di un materiale sotto carico statico nel tempo.
Matematicamente è l'inverso del modulo complesso di taglio e può essere considerata come una deformazione normalizzata sullo sforzo applicato.
Since the actual change in deformation depends on the load applied, it is normally referred to as compliance rather than deformation. Compliance is simply defined as the ratio of deformation to applied StressStress is defined as a level of force applied on a sample with a well-defined cross section. (Stress = force/area). Samples having a circular or rectangular cross section can be compressed or stretched. Elastic materials like rubber can be stretched up to 5 to 10 times their original length.stress and is marked with the letter J (J 0 = deformation/load). Due to this, creep curves can even then be compared if they were not measured under the same shear StressStress is defined as a level of force applied on a sample with a well-defined cross section. (Stress = force/area). Samples having a circular or rectangular cross section can be compressed or stretched. Elastic materials like rubber can be stretched up to 5 to 10 times their original length.stress applied.
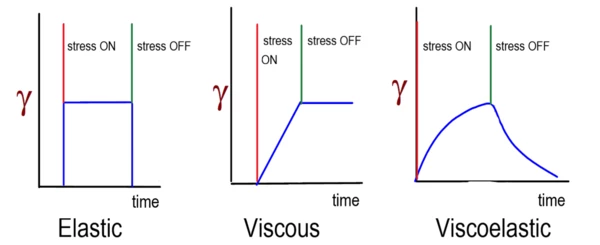
Since the actual change in deformation depends on the load applied, it is normally referred to as compliance rather than deformation. Compliance is simply defined as the ratio of deformation to applied StressStress is defined as a level of force applied on a sample with a well-defined cross section. (Stress = force/area). Samples having a circular or rectangular cross section can be compressed or stretched. Elastic materials like rubber can be stretched up to 5 to 10 times their original length.stress and is marked with the letter J (J 0 = deformation/load). Due to this, creep curves can even then be compared if they were not measured under the same shear StressStress is defined as a level of force applied on a sample with a well-defined cross section. (Stress = force/area). Samples having a circular or rectangular cross section can be compressed or stretched. Elastic materials like rubber can be stretched up to 5 to 10 times their original length.stress applied.
