Materiały polimerowe
Determination of the Oxidation Induction Time or Temperature: OIT and OOT
External influences such as UV radiation (light), temperature, atmospheric oxygen, atmospheric loads (e.g. impurities) or chemical/biological media lead to premature aging in organic materials, which might considerably influence their usage properties or might even lead to the failure of parts in which they are used as a component.
The most common cause of chemical aging (e.g. chain degradation) is OxidationOxidation can describe different processes in the context of thermal analysis.oxidation, which makes OxidationOxidation can describe different processes in the context of thermal analysis.oxidation stability an important criterion for applications with oils, fats, lubricants, fuels or plastics. The OxidationOxidation can describe different processes in the context of thermal analysis.oxidation stability can be determined via the OxidationOxidation can describe different processes in the context of thermal analysis.Oxidation Induction Temperature / OxidationOxidation can describe different processes in the context of thermal analysis.Oxidation Induction Time (Oxidative-Induction Time (OIT) and Oxidative-Onset Temperature (OOT)Oxidative Induction Time (isothermal OIT) is a relative measure of the resistance of a (stabilized) material to oxidative decomposition. Oxidative-Induction Temperature (dynamic OIT) or Oxidative-Onset Temperature (OOT) is a relative measure of the resistance of a (stabilized) material to oxidative decomposition.OIT) by means of differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) in standardized procedures.
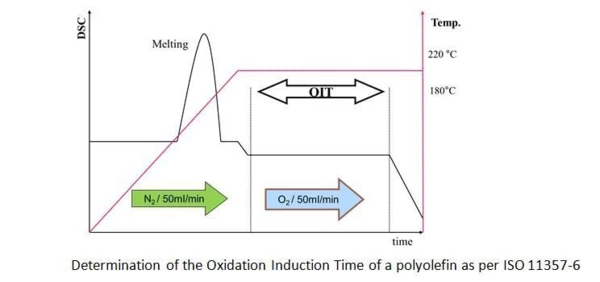
In practice, two different methods are used: dynamic and IsothermalTests at controlled and constant temperature are called isothermal.isothermal Oxidative-Induction Time (OIT) and Oxidative-Onset Temperature (OOT)Oxidative Induction Time (isothermal OIT) is a relative measure of the resistance of a (stabilized) material to oxidative decomposition. Oxidative-Induction Temperature (dynamic OIT) or Oxidative-Onset Temperature (OOT) is a relative measure of the resistance of a (stabilized) material to oxidative decomposition.OIT tests. In the dynamic technique, the sample is heated at a defined constant heating rate under oxidizing conditions until the reaction begins. The OxidationOxidation can describe different processes in the context of thermal analysis.Oxidation Induction Temperature Oxidative-Induction Time (OIT) and Oxidative-Onset Temperature (OOT)Oxidative Induction Time (isothermal OIT) is a relative measure of the resistance of a (stabilized) material to oxidative decomposition. Oxidative-Induction Temperature (dynamic OIT) or Oxidative-Onset Temperature (OOT) is a relative measure of the resistance of a (stabilized) material to oxidative decomposition.OIT (also called OxidationOxidation can describe different processes in the context of thermal analysis.Oxidation Onset Temperature Oxidative-Induction Time (OIT) and Oxidative-Onset Temperature (OOT)Oxidative Induction Time (isothermal OIT) is a relative measure of the resistance of a (stabilized) material to oxidative decomposition. Oxidative-Induction Temperature (dynamic OIT) or Oxidative-Onset Temperature (OOT) is a relative measure of the resistance of a (stabilized) material to oxidative decomposition.OOT) is the same as the extrapolated onset temperature of the EgzotermicznyA sample transition or a reaction is exothermic if heat is generated.exothermal DSC effect which occurs. In IsothermalTests at controlled and constant temperature are called isothermal.isothermal IOT tests, the materials to be investigated are first heated under a protective gas, then held at a constant temperature for several minutes to establish equilibrium and subsequently exposed to an atmosphere of oxygen or air. The time span from the first contact with oxygen until the beginning of OxidationOxidation can describe different processes in the context of thermal analysis.oxidation is called the OxidationOxidation can describe different processes in the context of thermal analysis.Oxidation Inductive Time Oxidative-Induction Time (OIT) and Oxidative-Onset Temperature (OOT)Oxidative Induction Time (isothermal OIT) is a relative measure of the resistance of a (stabilized) material to oxidative decomposition. Oxidative-Induction Temperature (dynamic OIT) or Oxidative-Onset Temperature (OOT) is a relative measure of the resistance of a (stabilized) material to oxidative decomposition.OIT
The procedure for the preparation, implementation and evaluation of measurements is described in detail in national and international standards such as ASTM D3895 (polyethylene), DIN EN 728 (plastic pipelines) or ISO 11357-6 (plastics). Generally, either open crucibles or crucibles with multiple piercings in the lids are used. For polyolefins like PE or PP, a longer Oxidative-Induction Time (OIT) and Oxidative-Onset Temperature (OOT)Oxidative Induction Time (isothermal OIT) is a relative measure of the resistance of a (stabilized) material to oxidative decomposition. Oxidative-Induction Temperature (dynamic OIT) or Oxidative-Onset Temperature (OOT) is a relative measure of the resistance of a (stabilized) material to oxidative decomposition.OIT time allows one to conclude that the OxidationOxidation can describe different processes in the context of thermal analysis.oxidation stability is better and the lifetime therefore longer.