Glossário
Stress-Strain Behavior
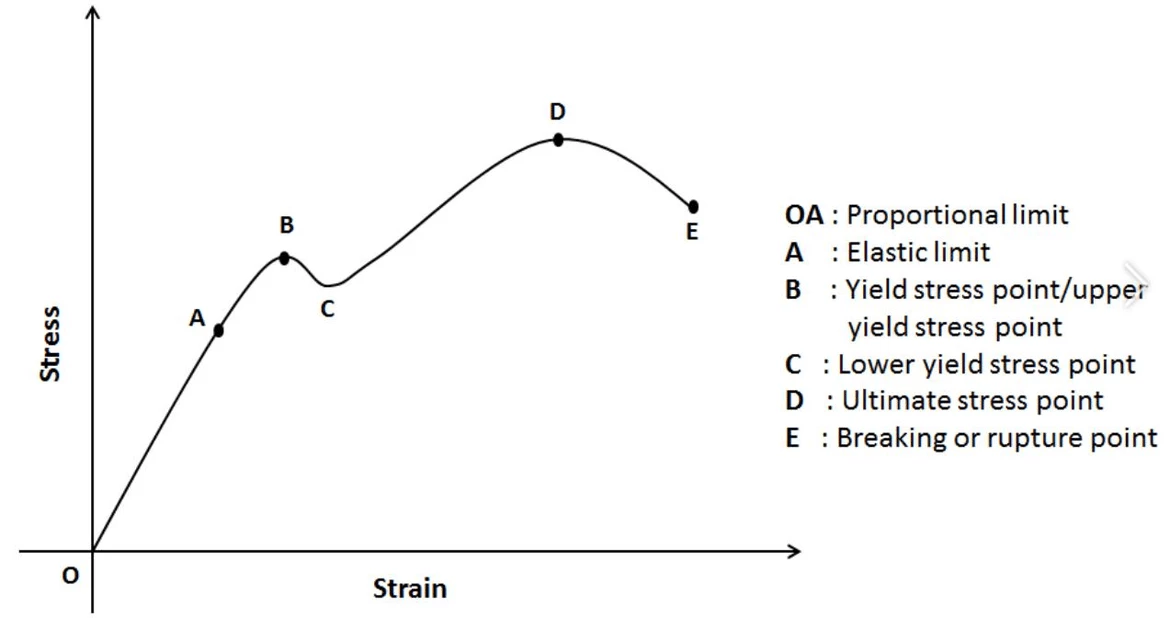
The figure shows a typical StressStress is defined as a level of force applied on a sample with a well-defined cross section. (Stress = force/area). Samples having a circular or rectangular cross section can be compressed or stretched. Elastic materials like rubber can be stretched up to 5 to 10 times their original length.stress-StrainStrain describes a deformation of a material, which is loaded mechanically by an external force or stress. Rubber compounds show creep properties, if a static load is applied.strain plot of an elastomer.
The most noticeable feature is its non-linearity, which takes place from A to E. Only in the range from 0 to A (normally the corresponding StrainStrain describes a deformation of a material, which is loaded mechanically by an external force or stress. Rubber compounds show creep properties, if a static load is applied.strain reaching the limit of linearity is not larger than 1 %), the StressStress is defined as a level of force applied on a sample with a well-defined cross section. (Stress = force/area). Samples having a circular or rectangular cross section can be compressed or stretched. Elastic materials like rubber can be stretched up to 5 to 10 times their original length.stress/StrainStrain describes a deformation of a material, which is loaded mechanically by an external force or stress. Rubber compounds show creep properties, if a static load is applied.strain ratio results in a constant number: the Elastic modulus.
This behavior can be measured with the DMA Eplexor®®.