Glossary
Polymorphism
Polymorphism is the ability of a solid material to form different crystalline structures (synonyms: forms, modifications).
Although different modifications of a polymorph have the same chemical structure, they differ in the physical properties such as:
- Solubility
- Melting Temperatures and EnthalpiesThe enthalpy of fusion of a substance, also known as latent heat, is a measure of the energy input, typically heat, which is necessary to convert a substance from solid to liquid state. The melting point of a substance is the temperature at which it changes state from solid (crystalline) to liquid (isotropic melt).Melting point
- Hygroscopicity
- Density
- Specific Heat Capacity (cp)Heat capacity is a material-specific physical quantity, determined by the amount of heat supplied to specimen, divided by the resulting temperature increase. The specific heat capacity is related to a unit mass of the specimen.Specific Heat capacity
This influences the processability of drug substances and the performance of drug products, such as:
- Stability
- Absorption into the body
- Dissolution (rate)
- Bioavailability
That is why polymorphism is an important topic for the pharmaceutical and also the food field.
The different modifications of a polymorph can be characterized with differential scanning calorimetry (DSC).

У вас есть вопросы?
Подходящие продукты для вашего измерения
Example
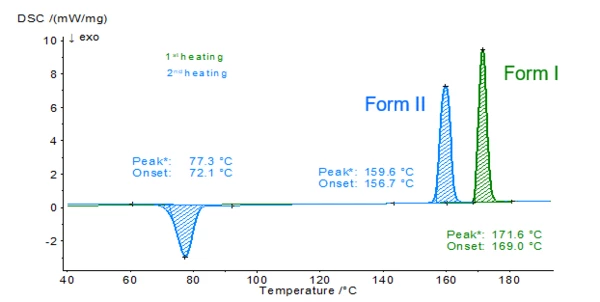
Polymorphism of Paracetamol
The figure depicts the two heatings of a paracetamol sample (initial mass: 2.6 mg). The heating rates as well as the cooling rate of the segment between both heatings amount to 10 K/min.
In the first heating, a peak at 169°C (onset temperature) is detected. This Melting Temperatures and EnthalpiesThe enthalpy of fusion of a substance, also known as latent heat, is a measure of the energy input, typically heat, which is necessary to convert a substance from solid to liquid state. The melting point of a substance is the temperature at which it changes state from solid (crystalline) to liquid (isotropic melt).melting temperature is typical for the monoclinic form I of paracetamol. [1]
During cooling at 10 K/min, no crystallization occurs. Crystallization takes place during the second heating at 72°C (onset temperature) to form another modification with Melting Temperatures and EnthalpiesThe enthalpy of fusion of a substance, also known as latent heat, is a measure of the energy input, typically heat, which is necessary to convert a substance from solid to liquid state. The melting point of a substance is the temperature at which it changes state from solid (crystalline) to liquid (isotropic melt).melting point at 157°C. This is typical for the orthorhombic form II of paracetamol [1].
