Highlights
The Method for the Determination of Thermal Diffusivity in the Thickness Range of Nanometer
Time DomainA time domain analysis is based on changes in physical signals related to time. A time-domain graph shows how a signal changes over time. In the case of thermoreflectance or the laser flash method, the detector signal (voltage change) is recorded – at a minimum – over the time range between the energy input and the signal maximum (e.g., RF mode) or as a function of the expected heat diffusion time (e.g., FF mode).Time Domain ThermoreflectanceThermoreflectance is a method for determining the thermal diffusivity and thermal conductivity of thin films with thicknesses in the nanometer range.Thermoreflectance Methods
The Method for the Determination of Thermal Diffusivity in the Thickness Range of Nanometer
With the significant progress in the design of electronic devices and the associated need for an efficient thermal management, accurate thermal diffusivity / Thermal ConductivityThermal conductivity (λ with the unit W/(m•K)) describes the transport of energy – in the form of heat – through a body of mass as the result of a temperature gradient (see fig. 1). According to the second law of thermodynamics, heat always flows in the direction of the lower temperature.thermal conductivity measurements in the nanometer range are more than ever crucial.
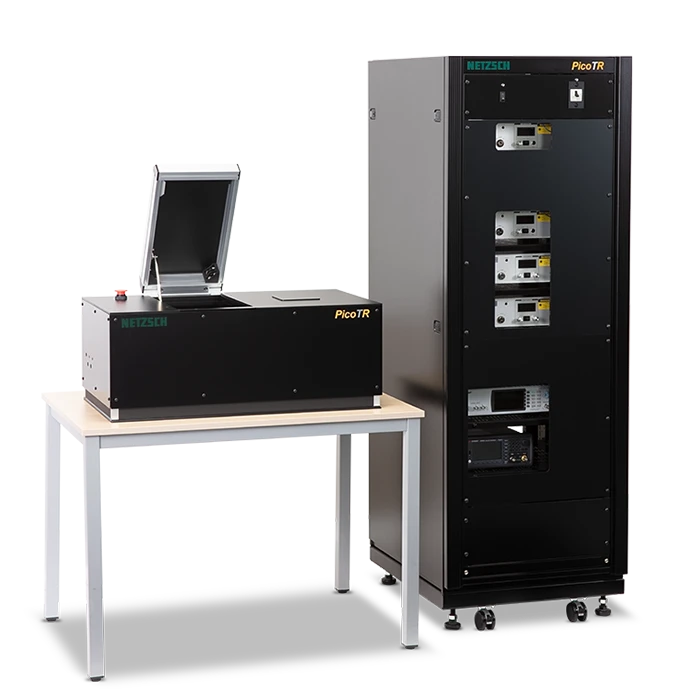
The National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), Japan, already responded to industrial requirements with the development of a “pulsed light heating ThermoreflectanceThermoreflectance is a method for determining the thermal diffusivity and thermal conductivity of thin films with thicknesses in the nanometer range.thermoreflectance method” in the early 90’s. PicoTherm Corporation was established in 2008 with the launch of a nano-second ThermoreflectanceThermoreflectance is a method for determining the thermal diffusivity and thermal conductivity of thin films with thicknesses in the nanometer range.thermoreflectance apparatus “NanoTR” and a pico-second ThermoreflectanceThermoreflectance is a method for determining the thermal diffusivity and thermal conductivity of thin films with thicknesses in the nanometer range.thermoreflectance apparatus “PicoTR”, which allows for absolute measurements of the thermal diffusivity of thin films in a thickness range of several 10 μm down into the nanometer range.
In October 2020, PicoTherm joined the NETZSCH Group as a subsidiary of NETZSCH Japan. In combination with our LFA systems, NETZSCH can now offer the solution for thin films in the nanometer range up to bulk materials in the range of mm.
With the significant progress in the design of electronic devices and the associated need for an efficient thermal management, accurate thermal diffusivity / Thermal ConductivityThermal conductivity (λ with the unit W/(m•K)) describes the transport of energy – in the form of heat – through a body of mass as the result of a temperature gradient (see fig. 1). According to the second law of thermodynamics, heat always flows in the direction of the lower temperature.thermal conductivity measurements in the nanometer range are more than ever crucial.
The National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), Japan, already responded to industrial requirements with the development of a “pulsed light heating ThermoreflectanceThermoreflectance is a method for determining the thermal diffusivity and thermal conductivity of thin films with thicknesses in the nanometer range.thermoreflectance method” in the early 90’s. PicoTherm Corporation was established in 2008 with the launch of a nano-second ThermoreflectanceThermoreflectance is a method for determining the thermal diffusivity and thermal conductivity of thin films with thicknesses in the nanometer range.thermoreflectance apparatus “NanoTR” and a pico-second ThermoreflectanceThermoreflectance is a method for determining the thermal diffusivity and thermal conductivity of thin films with thicknesses in the nanometer range.thermoreflectance apparatus “PicoTR”, which allows for absolute measurements of the thermal diffusivity of thin films in a thickness range of several 10 μm down into the nanometer range.
Method
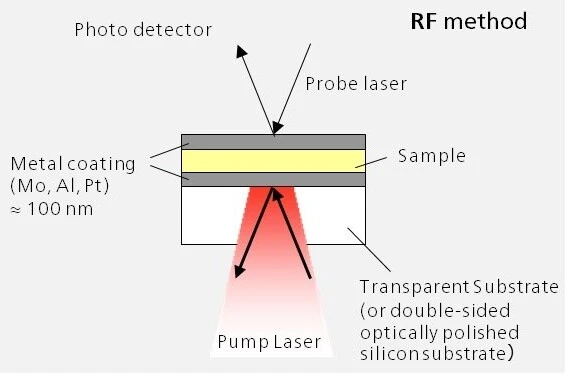
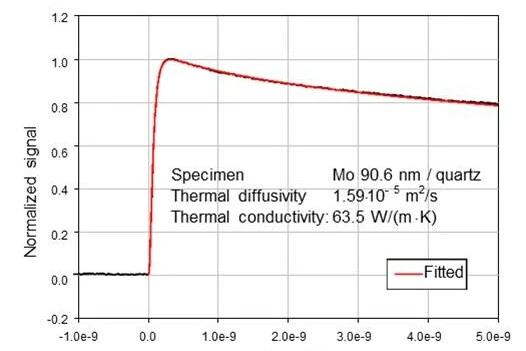
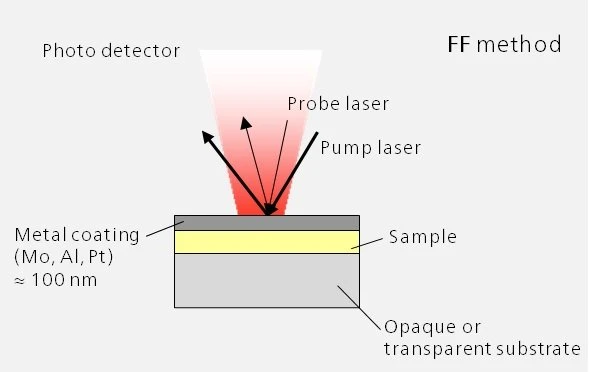
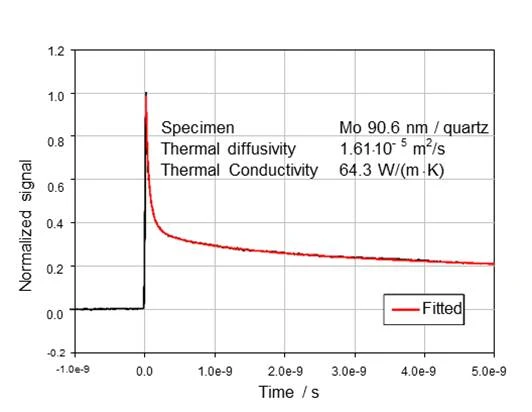
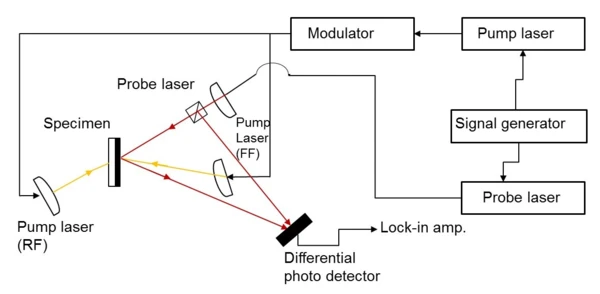
Time DomainA time domain analysis is based on changes in physical signals related to time. A time-domain graph shows how a signal changes over time. In the case of thermoreflectance or the laser flash method, the detector signal (voltage change) is recorded – at a minimum – over the time range between the energy input and the signal maximum (e.g., RF mode) or as a function of the expected heat diffusion time (e.g., FF mode).Time Domain ThermoreflectanceThermoreflectance is a method for determining the thermal diffusivity and thermal conductivity of thin films with thicknesses in the nanometer range.Thermoreflectance Methods – The Laser Flash method for thin films
With the PicoTR, laser pulses (pump laser) with a pulse width of 0.5 ps and a time period of 50 ns can be applied to the sample. The temperature response time is also detected by the sample laser.
PicoTR allows the user to easily switch between RT and FF mode.
PicoTR complies with the Japanese industry standards JIS R 1689 and JIS R 1690.
Specifications
| PicoTR | ||
|---|---|---|
| Pump Laser | Pulse width Wavelength Beam diameter | 0.5 ps 1550 nm 45 μm |
| Sample Laser | Pulse width Wavelength Beam diameter | 0.5 ps 775 nm 25 μm |
| Measured values | Thermal diffusivity and heat penetration coefficients, thermal resistance of intermediate layers | |
| Sample layer thickness (RF method) | Resin Ceramic Metal | 10 nm ... 100 nm 10 nm ... 300 nm 100 nm ... 900 nm |
| Sample layer thickness (FF method) | Thicker than 100 nm | |
| Substrates | Material Size Thickness | Opaque/transparent 10 ... 20 mm square 1 mm max. |
| Thermal diffusivity | Range | 0.01 ... 1000 mm²/s |
| Accuracy | ± 6.2 % with a measuring time of 40 min, for CRM 5808A in RF mode, 400 nm thickness | |
| Reproducibility | ± 5% | |
| Software | Calculation of thermal properties, multilayer analysis, database |
Software
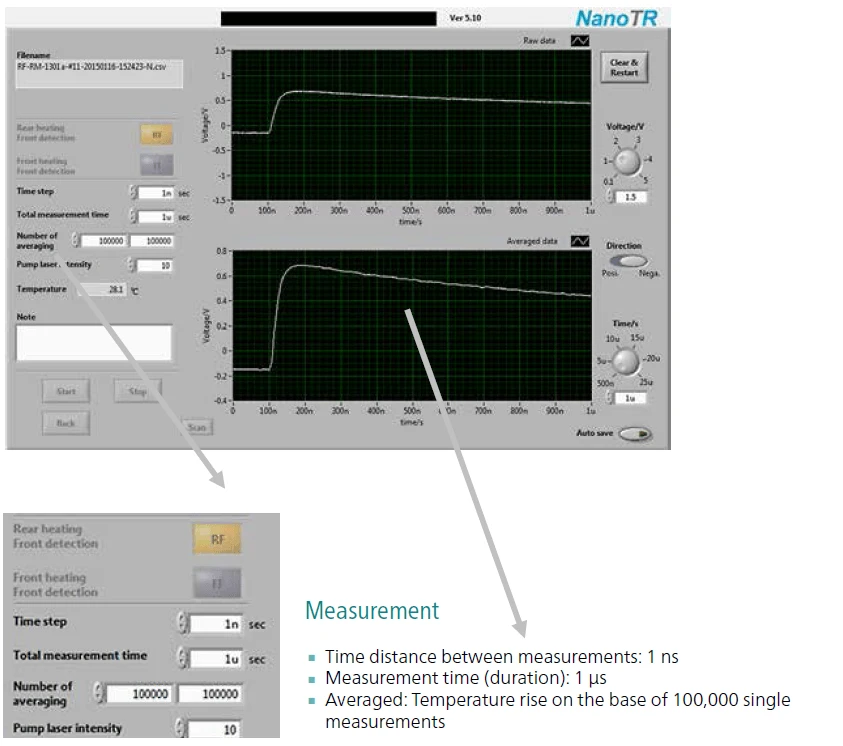
In-situ display and analyzing 100,000 shots
The state-of-the-art measurement/analysis software of NanoTR/PicoTR has an easy-to-handle user interface which allows for a precise determination of the thermal properties of thin films. The laser beam focusing can be adjusted by the software and CCD picture can be obtained.
NanoTR/PicoTR software runs under Microsoft Windows.
The plot shows that in 1 μs measurement time one measurement curve can be obtained.
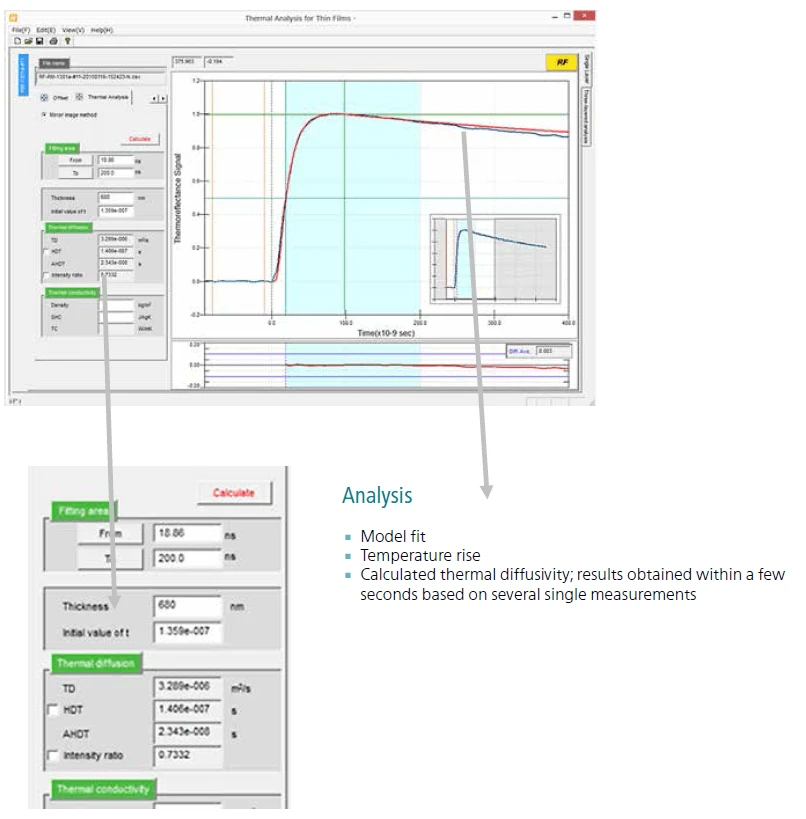
Obtaining results in minutes
Related Devices

Consultancy & Sales
Do you have further questions about the instrument or the method and would like to speak to a sales representative?
Service & Support
Do you already have an instrument and need technical support or spare parts?