용어집
탄성 및 탄성 계수
고무 탄성 또는 엔트로피 탄성은 외부에서 작용한 변형 또는 변형률(StrainStrain describes a deformation of a material, which is loaded mechanically by an external force or stress. Rubber compounds show creep properties, if a static load is applied.Strain)에 대한 고무 또는 엘라스토머의 저항을 나타냅니다.
고무 탄성은 엔트로피의 가역적 변화와 관련이 있습니다. 고분자 사슬을 따라 고무 또는 엘라스토머 매트릭스 내에서 이러한 가역적인 엔트로피 변화의 시작은 다음 측면으로 설명할 수 있습니다.
지그재그 엘라스토머 분자가 외력에 의해 확장되면, 사슬을 따라 이웃 분자 사이의 결합 각도가 변하게 됩니다. 마찰과정의 활성화 없이 이러한 작은 변화가 발생하면 변형 에너지는 필요하지 않습니다.
반면에 스트레칭은 분자 기반으로 배향이 발생하고 엔트로피(시스템 내 무질서)가 감소함을 의미 합니다.
외력이 제거되면, 환경으로부터 열에너지가 흡수되고 분자는 초기 방향으로 돌아갑니다. 결합 각도가 돌아가고 분자가 원래 모양으로 축소합니다.
탄성 계수(Elastic modulusThe complex modulus (elastic component), storage modulus, or G’, is the “real” part of the samples the overall complex modulus. This elastic component indicates the solid like, or in phase, response of the sample being measurement. Elastic modulus; Elasticity 라고도 함)는 응력(StressStress is defined as a level of force applied on a sample with a well-defined cross section. (Stress = force/area). Samples having a circular or rectangular cross section can be compressed or stretched. Elastic materials like rubber can be stretched up to 5 to 10 times their original length.Stress)이 가해질때 탄성적으로(즉, 비영구적으로) 변형되는 물체 또는 물질의 저항을 측정하는 양입니다.
물체의 탄성 계수는 탄성 변형 영역에서 응력-변형률 곡선(StressStress is defined as a level of force applied on a sample with a well-defined cross section. (Stress = force/area). Samples having a circular or rectangular cross section can be compressed or stretched. Elastic materials like rubber can be stretched up to 5 to 10 times their original length.Stress-StrainStrain describes a deformation of a material, which is loaded mechanically by an external force or stress. Rubber compounds show creep properties, if a static load is applied.Strain curve)의 기울기로 정의됩니다:[1] 더 단단한 재료는 더 높은 탄성 계수를 갖습니다. 탄성 계수는 다음 공식에 따라 정의됩니다.

궁금한 점이 있으신가요?
측정에 적합한 제품
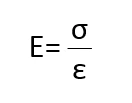
E modulus(탄성 모듈러스)는 DMA 242 Artemis® 와 DMA Eplexor®® 로 측정 가능합니다.
