Highlights
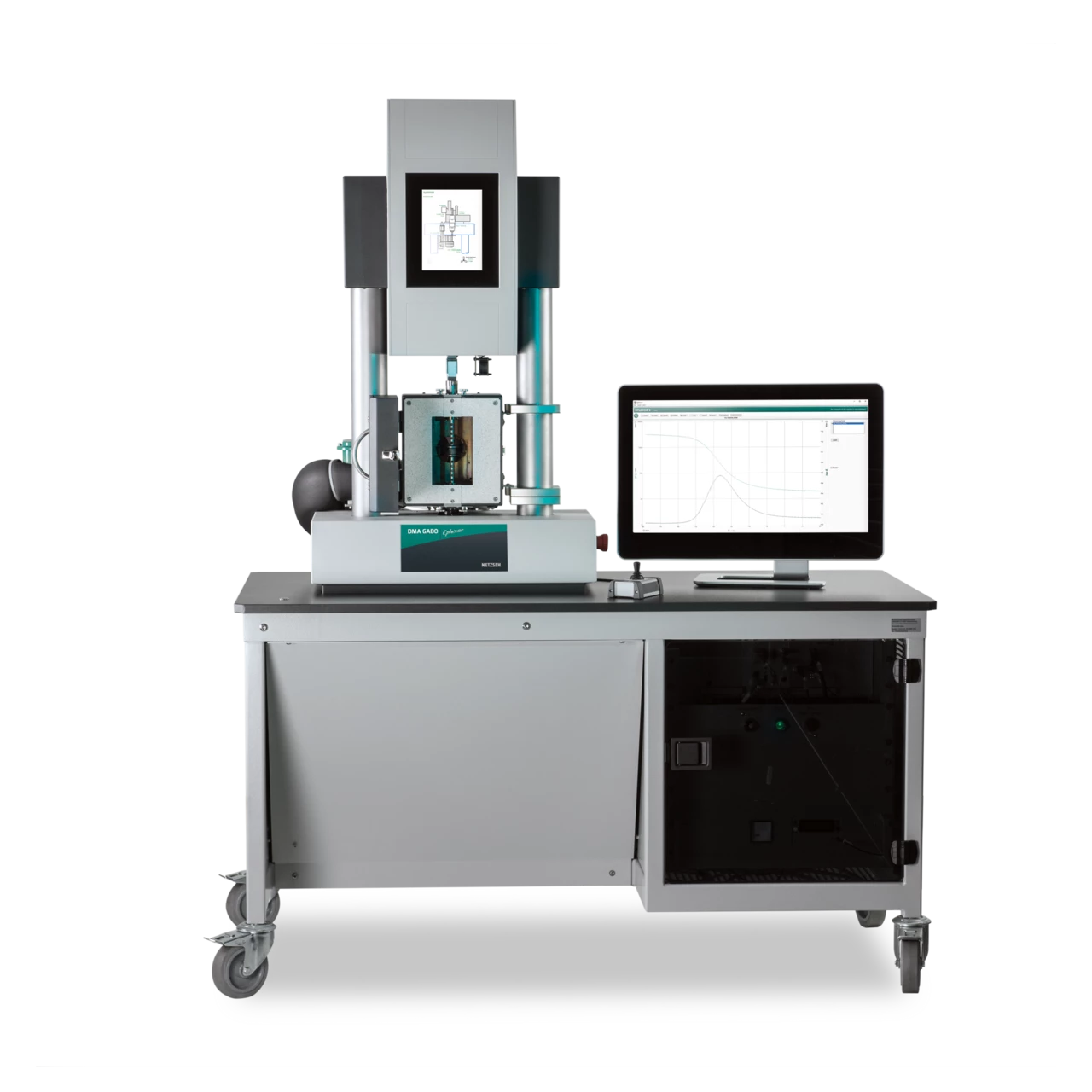
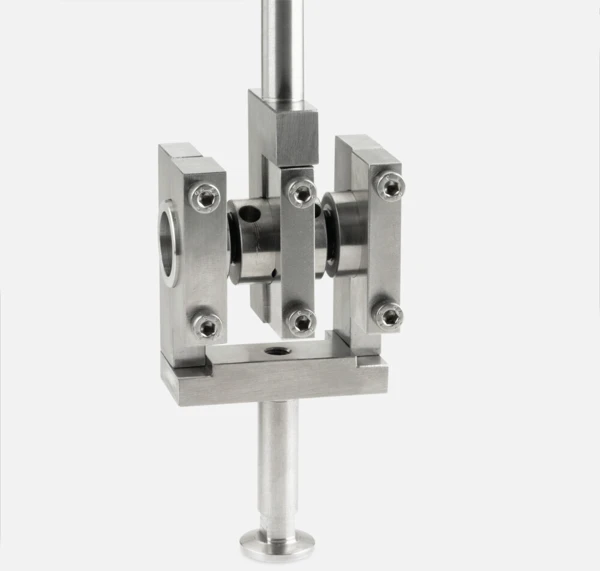
The testing instruments of the DMA GABO Eplexor® series up to ±500 N enable the dynamic mechanical (or static) characterization of a wide range of different materials including elastomers and polymers, composites, metals, glasses, ceramics, biomaterials and foods, adhesives, and liquids.
The modular design of the high-force DMA systems allows for measurements in the tension, compression, bending and shearing modes. The testing machines in this series differ from each other mainly in terms of their maximum dynamic force ranges of ±25 N, ±100 N, ±150 N and ±500 N.
Various add-on options make these testing machines a safe investment for the long-term.

Flexible and Set for the Future
...by means of a variety of force and StrainStrain describes a deformation of a material, which is loaded mechanically by an external force or stress. Rubber compounds show creep properties, if a static load is applied.strain sensors as well as furnaces which allow for easy upgrades to the basic system at any time after the first installation
High Force Levels
...allowing for static loads up to 1500 N and dynamic loads up to ± 500 N; especially meaningful for investigations on curable resins, elastomers, composites, metals, glasses or ceramics
Two Independent Drives
...featuring a servo motor for static and a shaker for dynamic loads
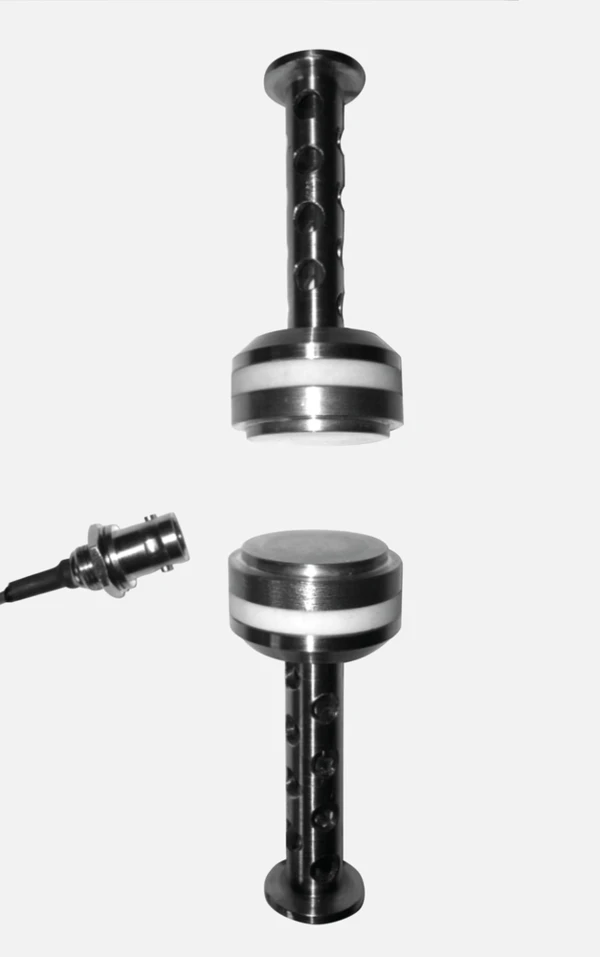
Interchangeable Force Sensors
...which can be easily changed out by the operator; nominal loads available ranging from ±10 N to ±2500 N
24/7 Operation via the Automatic Sample Changer
...for tension, compression and bending samples across the entire temperature range around the clock
Optimized for Temperature Sweeps on Large Samples
...thanks to uniform heating of even large samples with low Thermal ConductivityThermal conductivity (λ with the unit W/(m•K)) describes the transport of energy – in the form of heat – through a body of mass as the result of a temperature gradient (see fig. 1). According to the second law of thermodynamics, heat always flows in the direction of the lower temperature.thermal conductivity (e.g., large rubber specimens)
Highly Economic LN2 Cooling
...for low liquid nitrogen consumption
Simultaneous Determination of Dynamic Mechanical and Dielectric Material Properties
Accessories
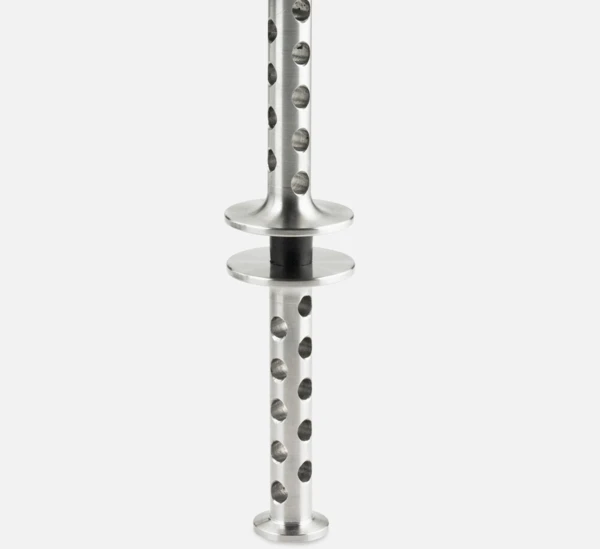
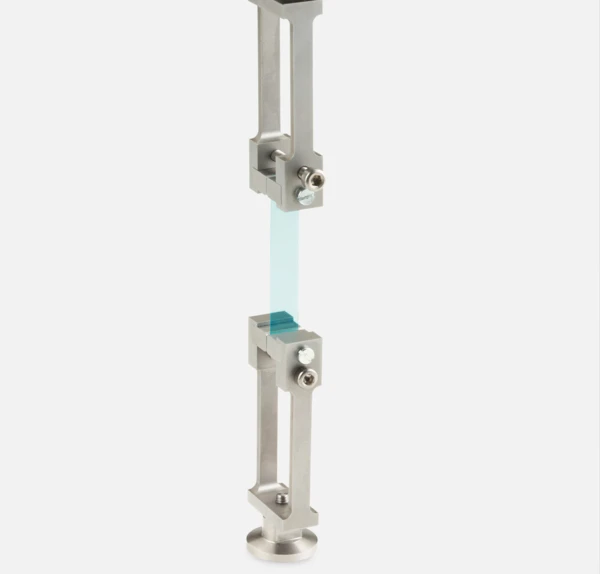
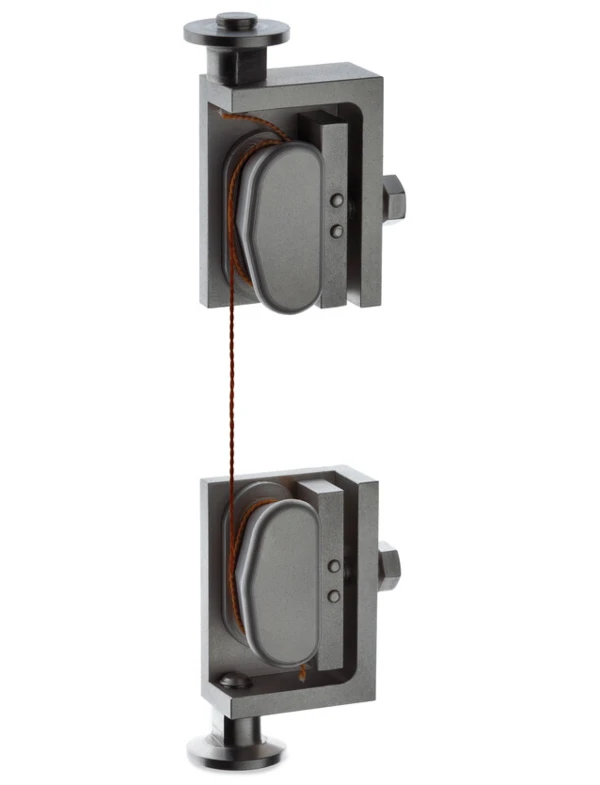
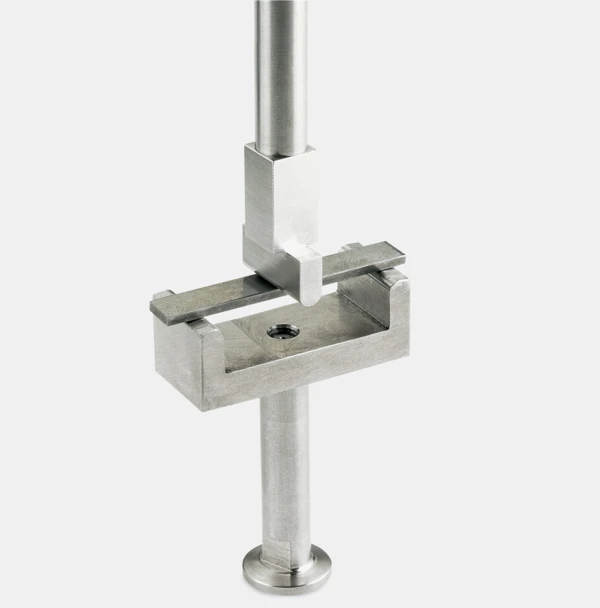
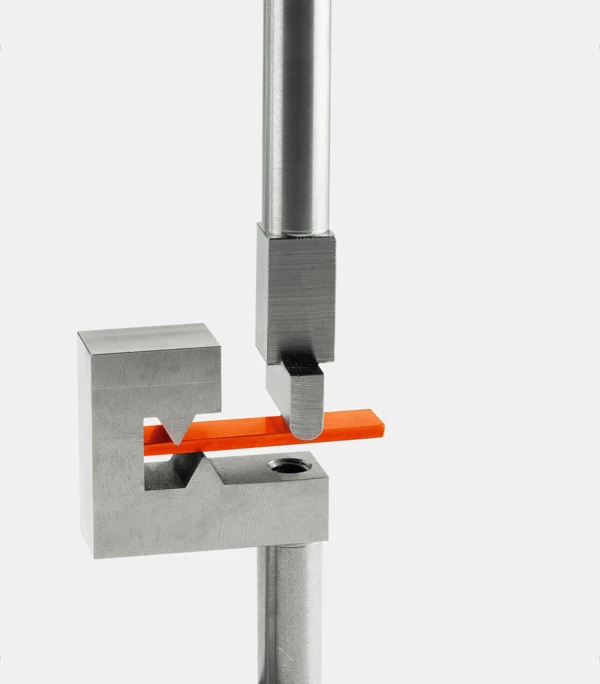
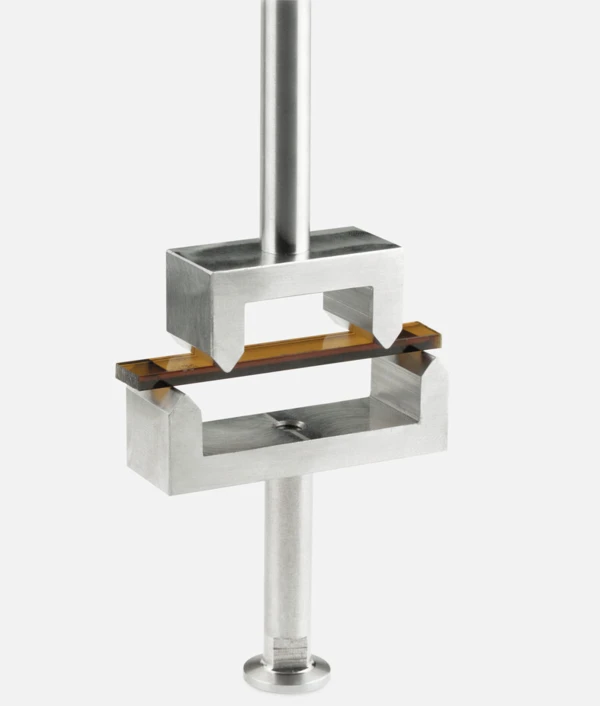
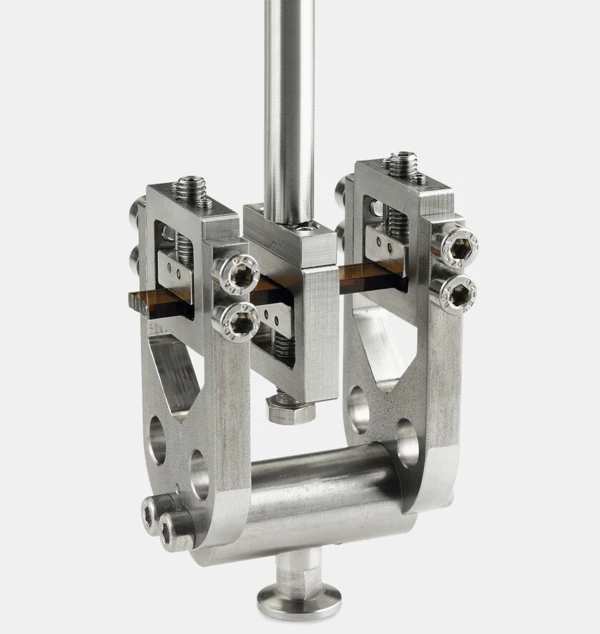
Sample Holders for a Variety of Applications
...from liquids via reinforced thermosets to metals and ceramics — all materials can be investigated with the DMA GABO Eplexor®.
DiPLEXOR® - Simultaneous DMA and DEA (on request)
...for the investigation of transport and RelaxationRelaxation은 고무에 일정한 변형률이 가해지면, 변형률을 유지하기 위해 필요한 힘은 일정하지는 않지만 시간에 따라 감소합니다. 이러한 특성을 ‘응력 완화’라고 부릅니다. 응력완화의 원인이 되는 과정은 물리적 또는 화학적 그리고 정상적인 조건 하에, 둘 다 동시에 일어날 수 있습니다. relaxation processes on the molecular level.
Humidity Generator (HYGROMATOR®)
...add-on serves to investigate the water uptake of samples such as plastics and biopolymers. With the humidity generator, it is possible to create relative humidity values of between 5% and 95% in the temperature range between 5°C and 95°C.
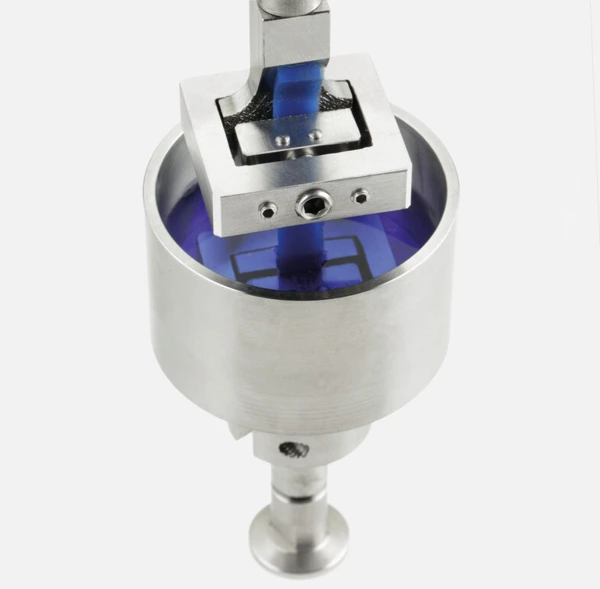
Immersion Bath
...even for measurements in the tension, compression and bending mode; for the investigation of aging or plasticizer effects caused by contact with water or oil.
Goodrich Flexometer Module
...for the optimization of the thermal properties and life cycle of tire mixtures; applies a cyclic load and measures the resulting temperature change due to heat build-up.
Cooling Options
...two different cooling systems are available including liquid nitrogen cooling to -160°C and air chiller to -60°C to use with the standard furnace
DMA Measurements in Reactive Atmospheres
...containment with fume hood for in-situ investigations protects the laboratory environment.
Method
The Dynamic Mechanical Thermal Analyzer applies forced periodic loads to the sample and analyzes the phase shift between this primary excitation and the material’s response. The response of an ideal elastic system (e.g., spring) on a sinusoidal load at a given frequency is of the same frequency and exactly in phase with the excitation. The situation changes in a real system: A phase shift (δ > 0°) between the primary excitation and response of the same frequency occurs in the case of linear visco-elastic materials (e.g., polymers).
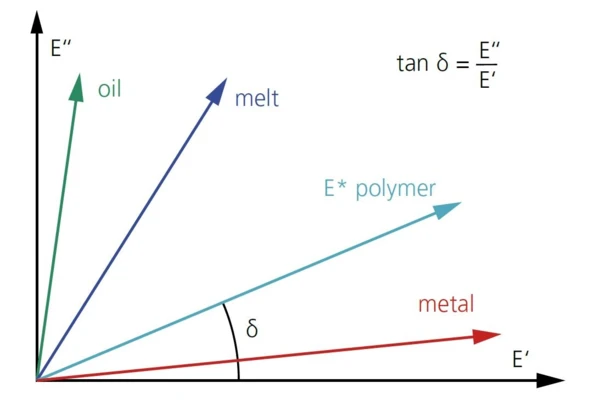
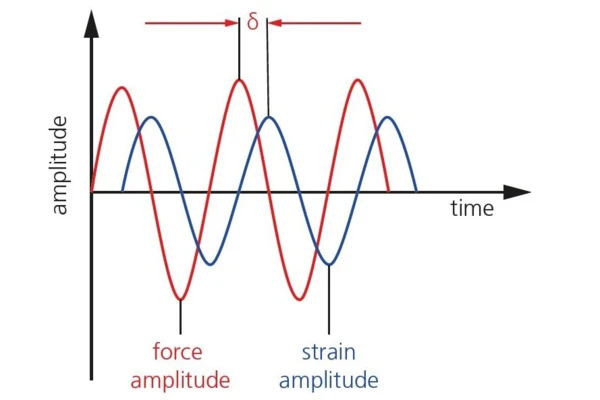
Elastic and non-elastic properties inherently describe the dynamic mechanical performance of the material. The storage modulus E’, the real part of the Complex ModulusThe complex modulus consists of two components, the storage and the loss moduli. The storage modulus (or Young’s modulus) describes the stiffness and the loss modulus describes the damping (or viscoelastic) behavior of the corresponding sample using the method of Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA). complex modulus E*, represents the elastic component; the Viscous modulusThe complex modulus (viscous component), loss modulus, or G’’, is the “imaginary” part of the samples the overall complex modulus. This viscous component indicates the liquid like, or out of phase, response of the sample being measurement. loss modulus E’’, the dissipated part, is the imaginary part. Depicted in the complex plane, the loss and storage modulus are the projections of the Complex ModulusThe complex modulus consists of two components, the storage and the loss moduli. The storage modulus (or Young’s modulus) describes the stiffness and the loss modulus describes the damping (or viscoelastic) behavior of the corresponding sample using the method of Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA). complex modulus onto the real and imaginary axis. The tangent of the angle between the real axis and the Complex ModulusThe complex modulus consists of two components, the storage and the loss moduli. The storage modulus (or Young’s modulus) describes the stiffness and the loss modulus describes the damping (or viscoelastic) behavior of the corresponding sample using the method of Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA). complex modulus (E*) represents the phase shift (tanδ) between the two.
Specifications
Technical Data
Temperature Range
Static force range
Frequency range
- Dynamic force range: ± 500 N, ± 150 N, ± 100 N, ± 25 N
- Force sensor: interchangeable; nominal forces available from ±10 N to ±2500 N
- Blade springs: counteract the static forces and allow for independent superposition of the dynamic forces
- Static displacement: 60 mm
- Dynamic displacement: available StrainStrain describes a deformation of a material, which is loaded mechanically by an external force or stress. Rubber compounds show creep properties, if a static load is applied.strain sensors: ± 1.5 mm, ± 3 mm and ± 6 mm (depending on the DMA GABO Eplexor® model)
- Supplementary analysis modes: CreepCreep은 일정한 힘 아래에서 시간과 온도에 따라 달라지는 소성 변형을 나타냅니다. 고무 화합물에 일정한 힘이 가해지면 가해진 힘에 인해 발생하는 초기 변형이 고정되지 않습니다. 변형은 시간이 지남에 따라 증가합니다creep, RelaxationRelaxation은 고무에 일정한 변형률이 가해지면, 변형률을 유지하기 위해 필요한 힘은 일정하지는 않지만 시간에 따라 감소합니다. 이러한 특성을 ‘응력 완화’라고 부릅니다. 응력완화의 원인이 되는 과정은 물리적 또는 화학적 그리고 정상적인 조건 하에, 둘 다 동시에 일어날 수 있습니다. relaxation, fatigue, heat build-up, Curing (Crosslinking Reactions)Literally translated, the term “crosslinking“ means “cross networking”. In the chemical context, it is used for reactions in which molecules are linked together by introducing covalent bonds and forming three-dimensional networks.curing, tensile tests, Rolling ResistanceThe rolling resistance is a force resisting the motion when a body is rolling across a surface. This determines the slip resistance of, e.g., car or truck tires.rolling resistance of tires, tackifying
- Max. sample dimensions (inside the standard furnace):
- tension: 80 mm x 10 mm x 10 mm (80 mm length)
- shear: ∅ 4 mm to 20 mm (standard: 10 mm)
- 3-point bending: up to 70 mm free bending length (up to 120 mm sample length)
- Automatic sample length detection or thickness determination possible in tensile, compression and bending geometries
Software
The comprehensive DMA GABO Eplexor® software is based on Windows operating systems. The extensive software package comprises data and curve analyses, hysteresis representation, master curve calculations, etc.
It also includes specific templates for tension, compression or bending tests.
The software features include:
- Frequency sweep of 0.001 Hz to 100 Hz (optional 0.0001 Hz and 200 Hz)
- Temperature sweep (controlled temperature variation at fixed frequency)
- Time sweep from 1 s to 107 s
- Correlated temperature and frequency sweep at IsothermalTests at controlled and constant temperature are called isothermal.isothermal steps
- Correlated dynamic and static StrainStrain describes a deformation of a material, which is loaded mechanically by an external force or stress. Rubber compounds show creep properties, if a static load is applied.strain amplitude sweeps; equidistantly or logarithmically subdivided
- Master curves (TTS, WLF, numeric mastering), segment tests
- Evaluation of Complex ModulusThe complex modulus consists of two components, the storage and the loss moduli. The storage modulus (or Young’s modulus) describes the stiffness and the loss modulus describes the damping (or viscoelastic) behavior of the corresponding sample using the method of Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA). complex modulus (E*, G*), storage modulus (E’, G’), Viscous modulusThe complex modulus (viscous component), loss modulus, or G’’, is the “imaginary” part of the samples the overall complex modulus. This viscous component indicates the liquid like, or out of phase, response of the sample being measurement. loss modulus (E’’, G’’) damping factor (t and δ) by temperature sweeps, StrainStrain describes a deformation of a material, which is loaded mechanically by an external force or stress. Rubber compounds show creep properties, if a static load is applied.strain and force sweeps, time sweeps, Glass Transition TemperatureThe glass transition is one of the most important properties of amorphous and semi-crystalline materials, e.g., inorganic glasses, amorphous metals, polymers, pharmaceuticals and food ingredients, etc., and describes the temperature region where the mechanical properties of the materials change from hard and brittle to more soft, deformable or rubbery.glass transition temperature, and optional CreepCreep은 일정한 힘 아래에서 시간과 온도에 따라 달라지는 소성 변형을 나타냅니다. 고무 화합물에 일정한 힘이 가해지면 가해진 힘에 인해 발생하는 초기 변형이 고정되지 않습니다. 변형은 시간이 지남에 따라 증가합니다creep, RelaxationRelaxation은 고무에 일정한 변형률이 가해지면, 변형률을 유지하기 위해 필요한 힘은 일정하지는 않지만 시간에 따라 감소합니다. 이러한 특성을 ‘응력 완화’라고 부릅니다. 응력완화의 원인이 되는 과정은 물리적 또는 화학적 그리고 정상적인 조건 하에, 둘 다 동시에 일어날 수 있습니다. relaxation, fatigue, energy loss, hysteresis, Payne/Mullins effect analysis and crack growth testing
- Determination of the thermal expansion in tension mode (optional)
- Prediction of the Rolling ResistanceThe rolling resistance is a force resisting the motion when a body is rolling across a surface. This determines the slip resistance of, e.g., car or truck tires.rolling resistance of tires (optional)

Consultancy & Sales
Do you have further questions about the device, the method and would you like to speak to a sales representative?
Service & Support
Do you already have an device and need technical support or spare parts?
Related Devices
- DMA 303 Eplexor®

- DMA 523 Eplexor®

- HBU 523 Gabometer

- Temperature Range up to 300°C
- Static force up to 6000N
- Static deformation up to 70 mm
- DMA Eplexor® HT Series up to 500 N












