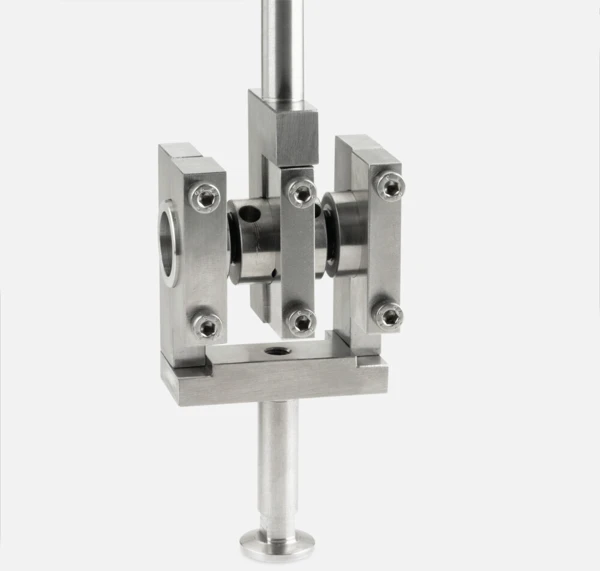
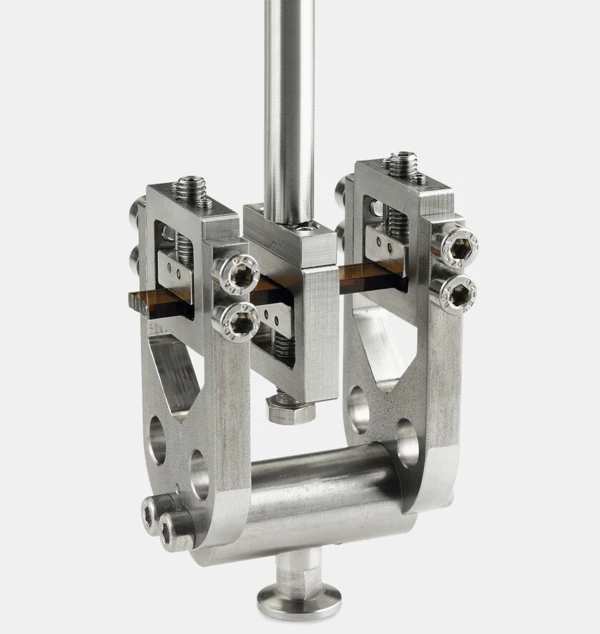
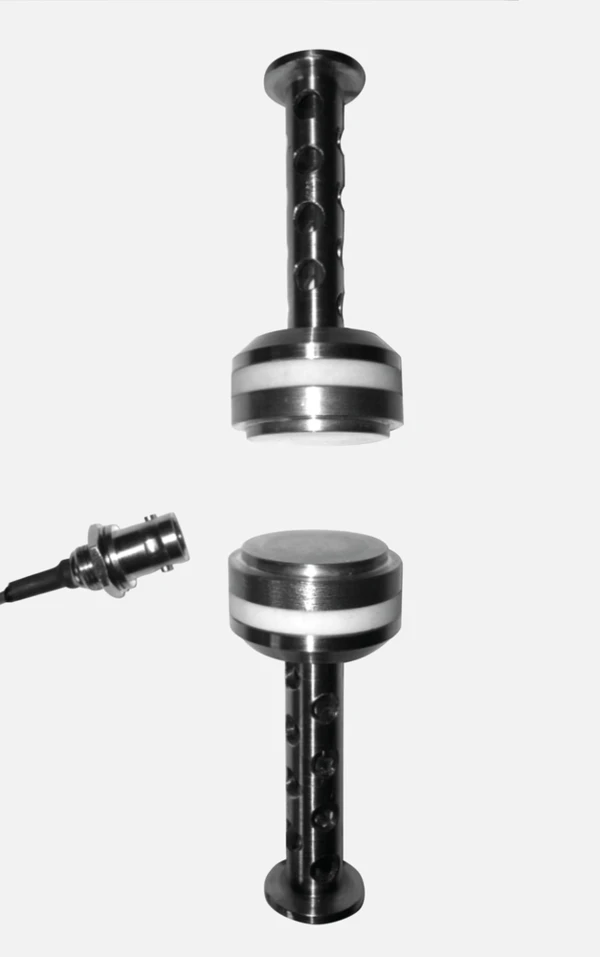
Highlights
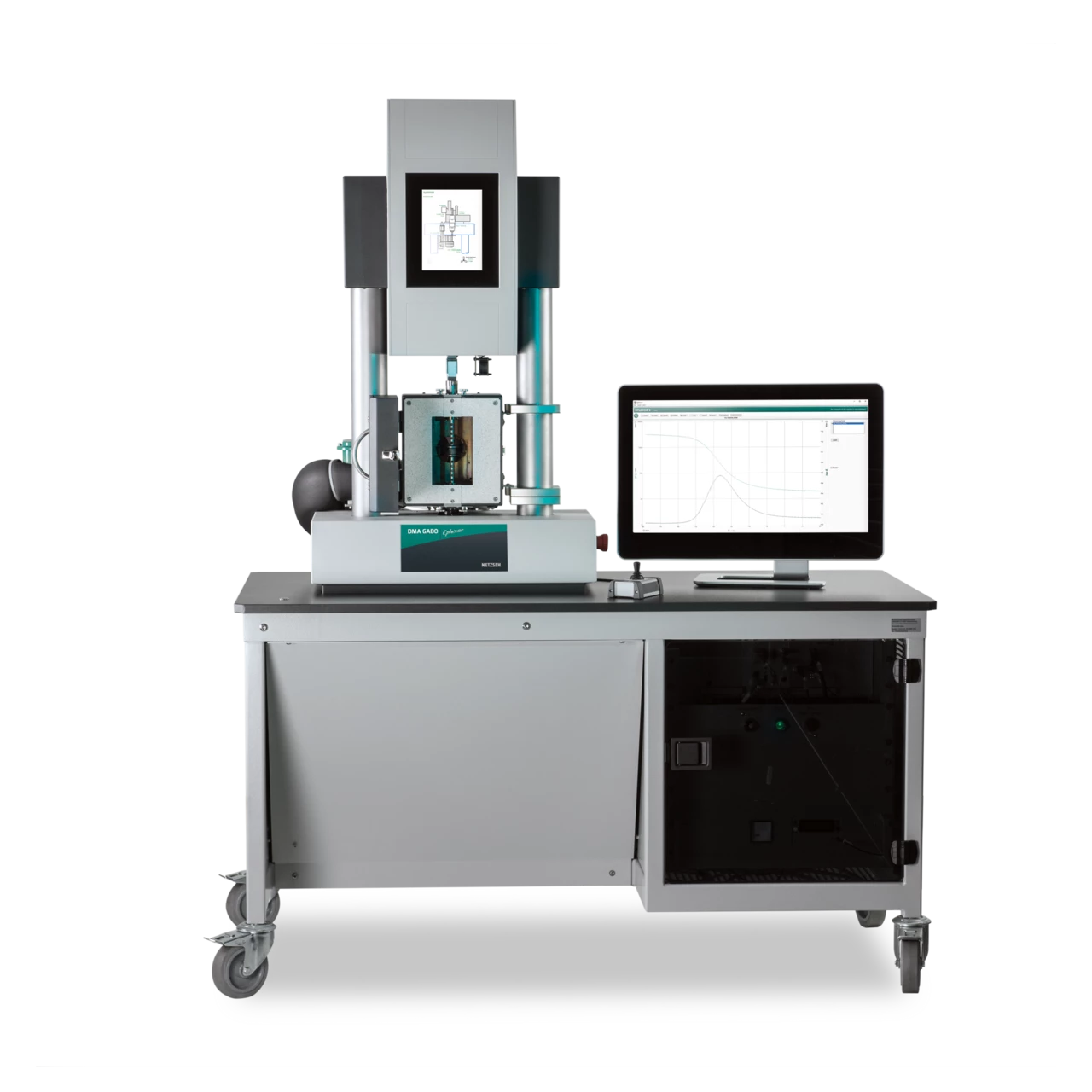
Les instruments de test de la série DMA GABO Eplexor® jusqu'à ± 500 N permettent la caractérisation mécanique dynamique (ou statique) d'une large gamme de matériaux différents dont les élastomères et polymères, composites, métaux, verres, céramiques, biomatériaux et aliments, adhésifs et liquides.
La conception modulable des systèmes DMA Haute Force permet des mesures dans les modes tension, compression, flexion et cisaillement. Les machines d'essai de cette série se distinguent principalement par leurs gammes de forces dynamiques maximales de ± 25 N, ± 100 N, ± 150 N et ± 500 N.
Diverses options complémentaires font de ces machines de test un investissement sûr à long terme.
Toutes les machines d'essai de cette série sont conformes aux normes telles que DIN 53513, ISO 6721/1, ISO 6721/4, ISO 6721/5, ISO 6721/6, ISO 4664, ASTM D4065 et ASTM D4473.

Flexible et prêt pour l'avenir
... au moyen d'une variété de capteurs de force et de ContrainteLa Contrainte est définie par un niveau de force appliquée sur un échantillon d’une section bien définie. (Contrainte = force/surface). Les échantillons qui possèdent une section rectangulaire ou circulaire peuvent être comprimés ou étirés. Les matériaux élastiques comme les élastomères peuvent être étirés jusqu’à 5 à 10 fois leur longueur initiale.contrainte ainsi que de fours qui permettent des mises à niveau faciles du système de base à tout moment après la première installation
Niveaux de force élevés
... permettant des charges statiques jusqu'à 1500 N et des charges dynamiques jusqu'à ± 500 N; particulièrement utile pour les recherches sur les résines durcissables, les élastomères, les composites, les métaux, les verres ou les céramiques
Deux systèmes indépendants
... avec servomoteur pour charges statiques et oscillateur pour charges dynamiques
Capteurs de force interchangeables
... qui peuvent être facilement changés par l'opérateur; charges nominales disponibles de ± 10 N à ± 2500 N
Accessories
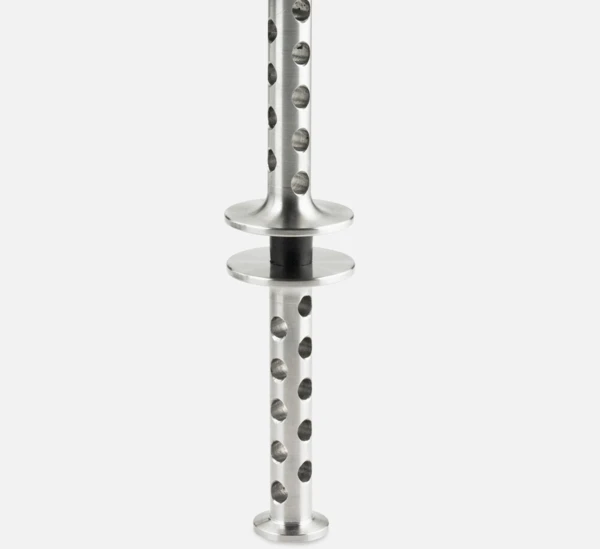
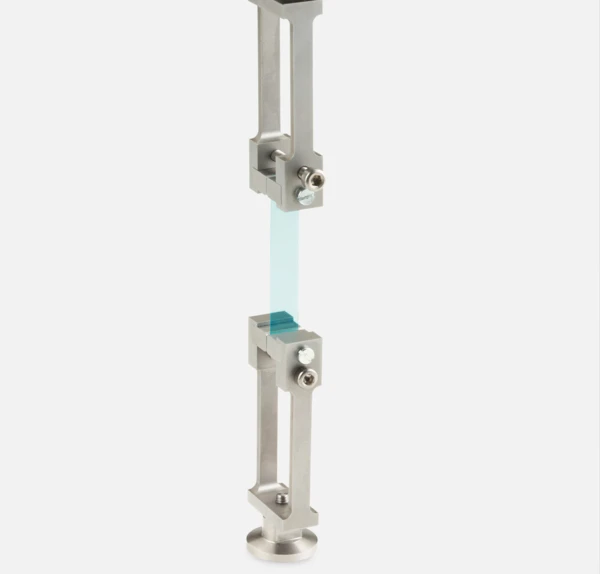
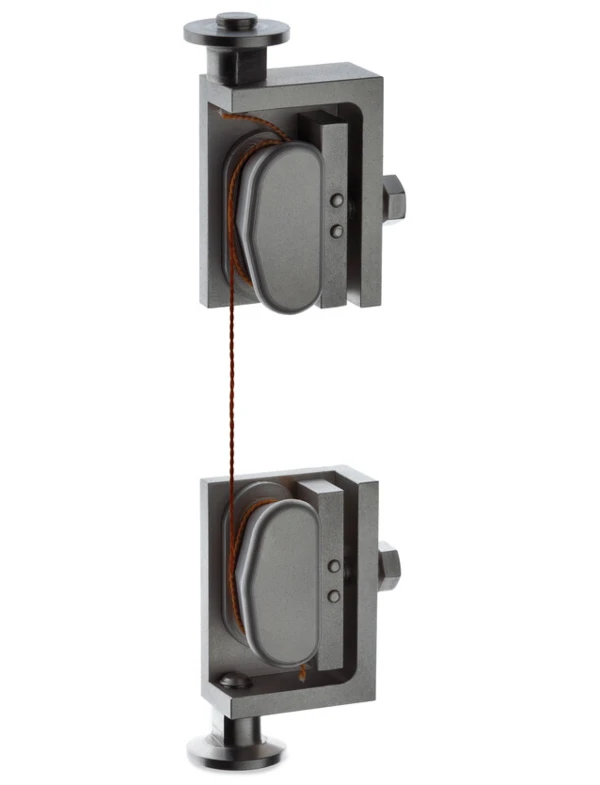
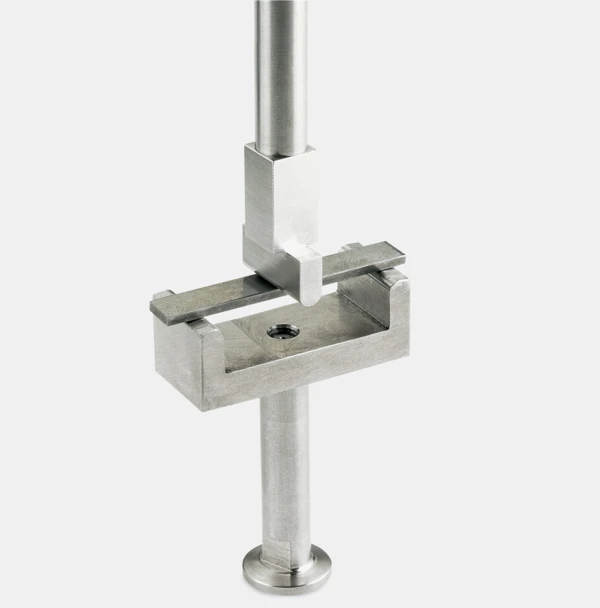
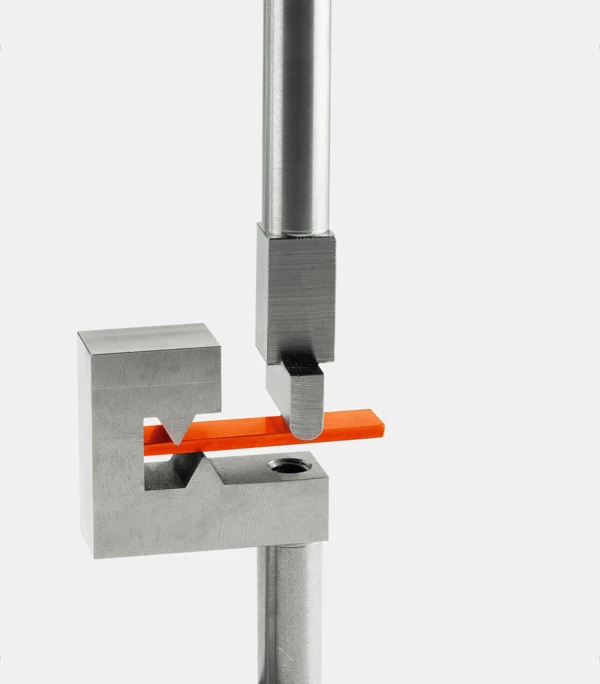
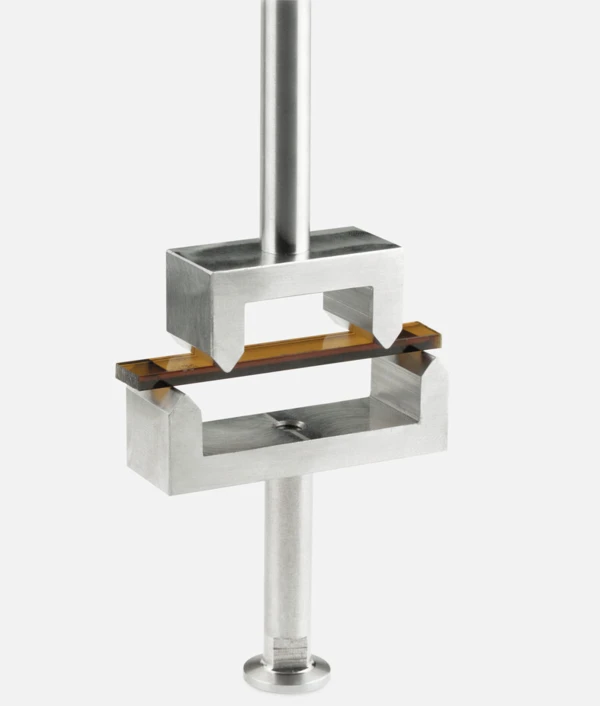
Sample Holders for a Variety of Applications
...from liquids via reinforced thermosets to metals and ceramics — all materials can be investigated with the DMA GABO Eplexor®.
DiPLEXOR® - Simultaneous DMA and DEA (on request)
...for the investigation of transport and RelaxationWhen a constant strain is applied to a rubber compound, the force necessary to maintain that strain is not constant but decreases with time; this behavior is known as stress relaxation. The process responsible for stress relaxation can be physical or chemical, and under normal conditions, both will occur at the same time. relaxation processes on the molecular level.
Humidity Generator (HYGROMATOR®)
...add-on serves to investigate the water uptake of samples such as plastics and biopolymers. With the humidity generator, it is possible to create relative humidity values of between 5% and 95% in the temperature range between 5°C and 95°C.
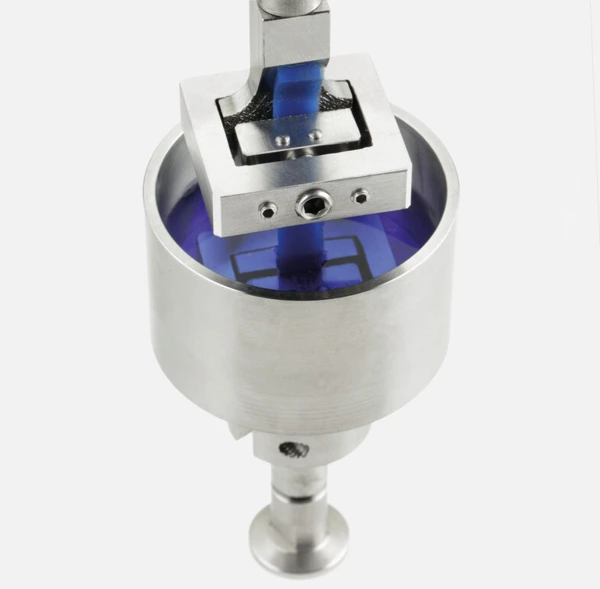
Immersion Bath
...even for measurements in the tension, compression and bending mode; for the investigation of aging or plasticizer effects caused by contact with water or oil.
Goodrich Flexometer Module
...for the optimization of the thermal properties and life cycle of tire mixtures; applies a cyclic load and measures the resulting temperature change due to heat build-up.
Cooling Options
...two different cooling systems are available including liquid nitrogen cooling to -160°C and air chiller to -60°C to use with the standard furnace
DMA Measurements in Reactive Atmospheres
...containment with fume hood for in-situ investigations protects the laboratory environment.
Method
The Dynamic Mechanical Thermal Analyzer applies forced periodic loads to the sample and analyzes the phase shift between this primary excitation and the material’s response. The response of an ideal elastic system (e.g., spring) on a sinusoidal load at a given frequency is of the same frequency and exactly in phase with the excitation. The situation changes in a real system: A phase shift (δ > 0°) between the primary excitation and response of the same frequency occurs in the case of linear visco-elastic materials (e.g., polymers).
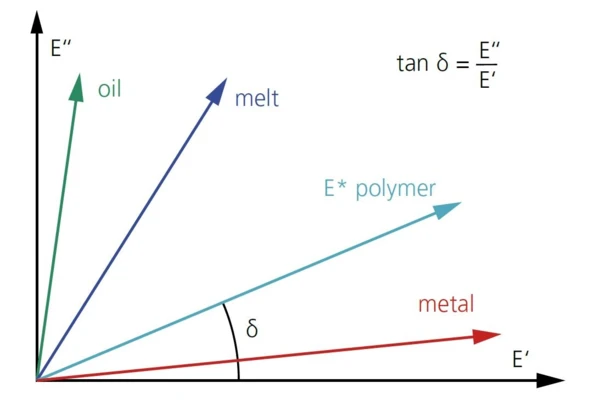
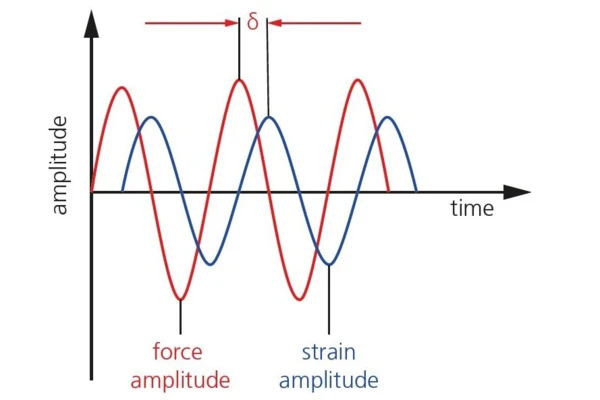
Elastic and non-elastic properties inherently describe the dynamic mechanical performance of the material. The storage modulus E’, the real part of the complex modulus E*, represents the elastic component; the Viscous modulusThe complex modulus (viscous component), loss modulus, or G’’, is the “imaginary” part of the samples the overall complex modulus. This viscous component indicates the liquid like, or out of phase, response of the sample being measurement. loss modulus E’’, the dissipated part, is the imaginary part. Depicted in the complex plane, the loss and storage modulus are the projections of the complex modulus onto the real and imaginary axis. The tangent of the angle between the real axis and the complex modulus (E*) represents the phase shift (tanδ) between the two.

Demander un devis
Specifications
Technical Data
Temperature Range
Static force range
Frequency range
- Dynamic force range: ± 500 N, ± 150 N, ± 100 N, ± 25 N
- Force sensor: interchangeable; nominal forces available from ±10 N to ±2500 N
- Blade springs: counteract the static forces and allow for independent superposition of the dynamic forces
- Static displacement: 60 mm
- Dynamic displacement: available strain sensors: ± 1.5 mm, ± 3 mm and ± 6 mm (depending on the DMA GABO Eplexor® model)
- Supplementary analysis modes: creep, RelaxationWhen a constant strain is applied to a rubber compound, the force necessary to maintain that strain is not constant but decreases with time; this behavior is known as stress relaxation. The process responsible for stress relaxation can be physical or chemical, and under normal conditions, both will occur at the same time. relaxation, fatigue, heat build-up, curing, tensile tests, Rolling ResistanceThe rolling resistance is a force resisting the motion when a body is rolling across a surface. This determines the slip resistance of, e.g., car or truck tires.rolling resistance of tires, tackifying
- Max. sample dimensions (inside the standard furnace):
- tension: 80 mm x 10 mm x 10 mm (80 mm length)
- shear: ∅ 4 mm to 20 mm (standard: 10 mm)
- 3-point bending: up to 70 mm free bending length (up to 120 mm sample length)
- Automatic sample length detection or thickness determination possible in tensile, compression and bending geometries
Software
The comprehensive DMA GABO Eplexor® software is based on Windows operating systems. The extensive software package comprises data and curve analyses, hysteresis representation, master curve calculations, etc.
It also includes specific templates for tension, compression or bending tests.
The software features include:
- Frequency sweep of 0.001 Hz to 100 Hz (optional 0.0001 Hz and 200 Hz)
- Temperature sweep (controlled temperature variation at fixed frequency)
- Time sweep from 1 s to 107 s
- Correlated temperature and frequency sweep at isothermal steps
- Correlated dynamic and static strain amplitude sweeps; equidistantly or logarithmically subdivided
- Master curves (TTS, WLF, numeric mastering), segment tests
- Evaluation of complex modulus (E*, G*), storage modulus (E’, G’), Viscous modulusThe complex modulus (viscous component), loss modulus, or G’’, is the “imaginary” part of the samples the overall complex modulus. This viscous component indicates the liquid like, or out of phase, response of the sample being measurement. loss modulus (E’’, G’’) damping factor (t and δ) by temperature sweeps, strain and force sweeps, time sweeps, Température de Transition VitreuseThe glass transition is one of the most important properties of amorphous and semi-crystalline materials, e.g., inorganic glasses, amorphous metals, polymers, pharmaceuticals and food ingredients, etc., and describes the temperature region where the mechanical properties of the materials change from hard and brittle to more soft, deformable or rubbery.glass transition temperature, and optional creep, RelaxationWhen a constant strain is applied to a rubber compound, the force necessary to maintain that strain is not constant but decreases with time; this behavior is known as stress relaxation. The process responsible for stress relaxation can be physical or chemical, and under normal conditions, both will occur at the same time. relaxation, fatigue, energy loss, hysteresis, Payne/Mullins effect analysis and crack growth testing
- Determination of the thermal expansion in tension mode (optional)
- Prediction of the Rolling ResistanceThe rolling resistance is a force resisting the motion when a body is rolling across a surface. This determines the slip resistance of, e.g., car or truck tires.rolling resistance of tires (optional)

Consultancy & Sales
Do you have further questions about the device, the method and would you like to speak to a sales representative?
Service & Support
Do you already have an device and need technical support or spare parts?
Related Devices
- DMA 303 Eplexor®

- Wide Temperature Range from -170°C to 800°C
- Precise Forces up to 50 N Dynamic and Static
- Accessories for Multiple Measuring Modes and a Variety of Sample Holders
- DMA 523 Eplexor®

- Static and dynamic force levels from max. ± 2000 N to max. ± 4000 N
- Sample Holders for a Variety of Applications
- Unrivaled Temperature Range from -160°C to 500°C
- HBU 523 Gabometer

- Temperature Range up to 300°C
- Static force up to 6000N
- Static deformation up to 70 mm
- DMA Eplexor® HT Series up to 500 N












