용어집. v
Creep (DMA)
Creep은 일정한 힘 아래에서 시간과 온도에 따라 달라지는 소성 변형을 나타냅니다. 고무 화합물에 일정한 힘이 가해지면 가해진 힘에 인해 발생하는 초기 변형이 고정되지 않습니다. 변형은 시간이 지남에 따라 증가합니다
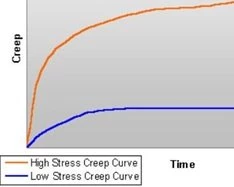
Creep-Behavior
Creep behavior is the term for describing the creep processes taking place in different materials.
Depicted in the figure are the characteristics of a high-StressStress is defined as a level of force applied on a sample with a well-defined cross section. (Stress = force/area). Samples having a circular or rectangular cross section can be compressed or stretched. Elastic materials like rubber can be stretched up to 5 to 10 times their original length.stress and low-StressStress is defined as a level of force applied on a sample with a well-defined cross section. (Stress = force/area). Samples having a circular or rectangular cross section can be compressed or stretched. Elastic materials like rubber can be stretched up to 5 to 10 times their original length.stress creep curve. The figure shows creep over time.
RelaxationRelaxation은 고무에 일정한 변형률이 가해지면, 변형률을 유지하기 위해 필요한 힘은 일정하지는 않지만 시간에 따라 감소합니다. 이러한 특성을 ‘응력 완화’라고 부릅니다. 응력완화의 원인이 되는 과정은 물리적 또는 화학적 그리고 정상적인 조건 하에, 둘 다 동시에 일어날 수 있습니다. Relaxation, creep and Creep RecoveryCreep recovery is the ratio of the recoverable creep compliance to initial creep compliance given in percent. Often in MSCR (multiple stress creep recovery) testing, creep recovery is considered a performance indicator with more recovery indicating a binder less prone to rutting.creep recovery processes can be measured with the NETZSCH DMA Eplexor®® and DMA 242 Artemis®.


