Introduction
Coin cell is a small single cell in the shape of a cylinder or button. It is used in many everyday small portable electronics devices including watches, calculators, remote controls, electronic toys, small LED flashlights etc. It is manufactured in huge quantity every year around the world. There are several different types of coin cells based on chemical composition including silver cell, alkaline cell, zinc-air cell and lithium cell. Some are not rechargeable, while some are rechargeable for example lithium-ion coin cell or Ni-MH coin cell. Compared with the non-rechargeable, disposable cells, the rechargeable cells cost more initially, but the extended lifetime of rechargeable cells make them a better investment for consumers. Plus the rechargeable cells have less impact on the environment as the battery chemicals are often toxic and can pollute environment. Also lithium-ion rechargeable cell offers higher power DensityThe mass density is defined as the ratio between mass and volume. density and capacity.
Many parameters will influence the performance of rechargeable coin cell including temperature and cycling conditions. It is very important for coin cell manufacturer to know the heat generation during charging/discharging cycles in order to understand the cell energy efficiency and improve cell performance and lifetime. It is also imperative to be able to examine the safety of the whole coin cell when it is subjected to high temperature. This application note shows IsothermalTests at controlled and constant temperature are called isothermal.isothermal cycling of lithium ion coin cell in a novel DSC-like sysetm dedicated to the research and quality control of coin cell battery.
Instrumentation
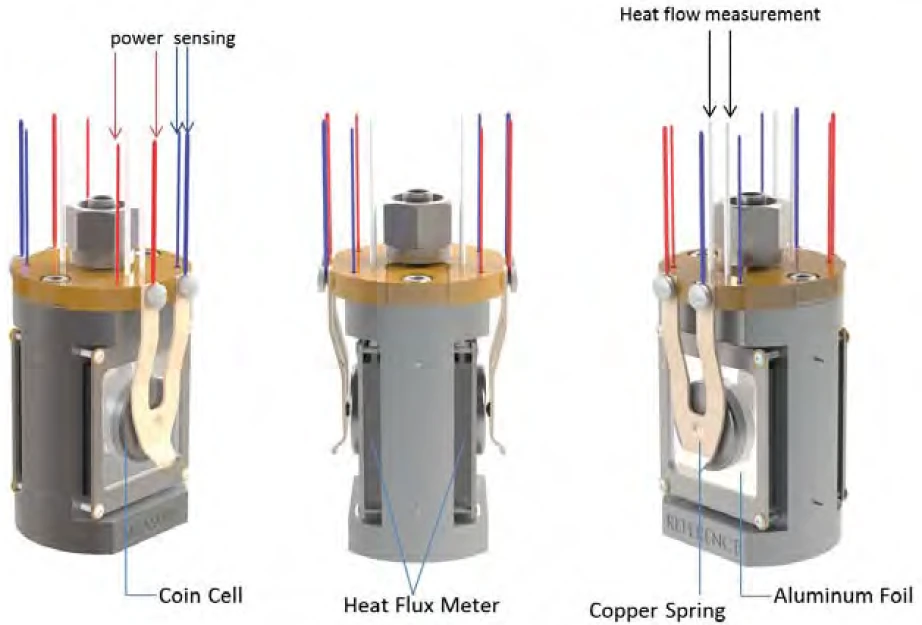
The new instrument used is the high temperature Coin Cell ModuleA calorimeter module being part of the Multiple Module Calorimeter (MMC) allowing for scanning and isothermal tests of complete coins of variable size. The DSC-like twin design gives a differential signal of the heat signature during a heating ramp or charging and discharging of batteries.coin cell module on NETZSCH Multiple Module Calorimeter (MMC)A multiple mode calorimeter device consisting of a base unit and exchangeable modules. One module is prepared for accelerating rate calorimetry (ARC), the ARC-Module. A second one is used for scanning tests (Scanning Module) and a third one is related to battery testing for coin cells (Coin Cell Module).MMC 274 Nexus® (fig 1). It is the only DSC-like system for research and quality control of coin cell battery in the world. The key component of this new instrument is the sensor (fig 2 and 3). It features an innovative differential measurement design based on thermopile for improved sensitivity and stability of heat flow measurement.
It is designed to hold a whole coin cell battery as sample. External battery cycler can be connected to the instrument easily through a plug-and-play LEMO connector. IsothermalTests at controlled and constant temperature are called isothermal.Isothermal cycling of coin cell can be easily performed under various charging/discharging conditions. The new instrument can also do DSC scanning on a whole coin cell which was not possible before.


Results
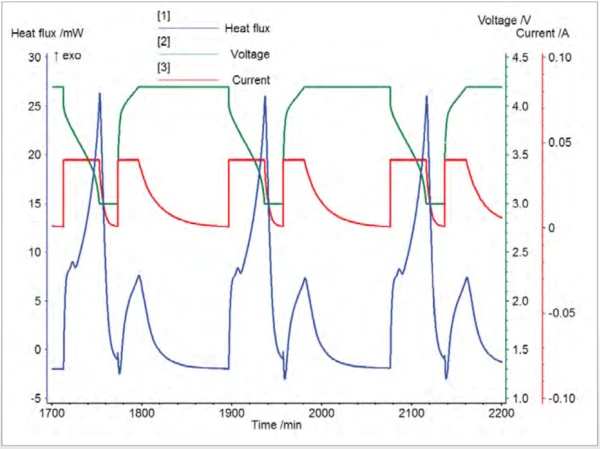
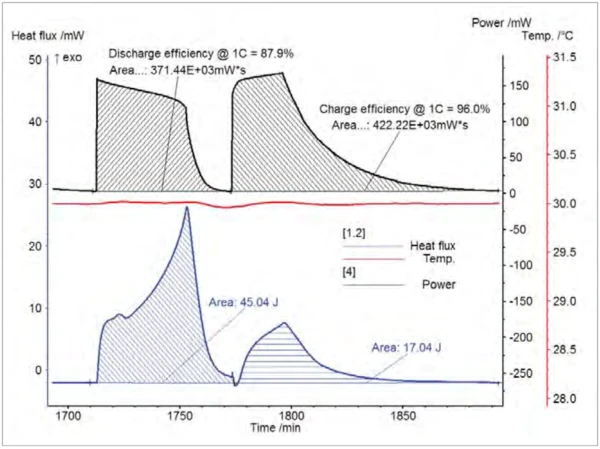
A LiR2032 lithium ion coin cell battery was used as a sample and an aluminum block of same size was used as reference. The cell was maintained at 40°C throughout the experiment. Constant Current-Constant Voltage (CCCV) charging and discharging was carried out at 40 mA from 4.2 V to 3.0 V using an external battery cycler. Several cycles were performed and the heat flow data were quite reproducible. The data shows that charging is characterized by a short endotherm followed by a small ExothermicA sample transition or a reaction is exothermic if heat is generated.exothermic reaction while discharging is characterized by a long ExothermicA sample transition or a reaction is exothermic if heat is generated.exothermic reaction (fig. 4). The data can be easily integrated to get the electrical energy in or out of the coin cell and the heat released at the same time (fig. 5). This makes the calculation of battery efficiency straightforward for both charging and discharging processes as shown in figure 4. Without the heat information from HT Coin Cell ModuleA calorimeter module being part of the Multiple Module Calorimeter (MMC) allowing for scanning and isothermal tests of complete coins of variable size. The DSC-like twin design gives a differential signal of the heat signature during a heating ramp or charging and discharging of batteries.Coin Cell calorimetry, the efficiency can only be estimated.
Conclusion
The new high-temperature Coin Cell ModuleA calorimeter module being part of the Multiple Module Calorimeter (MMC) allowing for scanning and isothermal tests of complete coins of variable size. The DSC-like twin design gives a differential signal of the heat signature during a heating ramp or charging and discharging of batteries.coin cell module on Multiple Module Calorimeter (MMC)A multiple mode calorimeter device consisting of a base unit and exchangeable modules. One module is prepared for accelerating rate calorimetry (ARC), the ARC-Module. A second one is used for scanning tests (Scanning Module) and a third one is related to battery testing for coin cells (Coin Cell Module).MMC 274 Nexus® is a dedicated calorimeter for coin cell analysis. Its innovative sensor incorporates differential principle for high quality data. The sensor is designed to accommodate commercial coin cell battery of different size. A whole coin cell battery can be easily loaded and unloaded. The flexible software enables both IsothermalTests at controlled and constant temperature are called isothermal.isothermal and scanning modes for complete characterization of coin cell. Thanks to this new instrument, accurate heat flow information can be obtained during charging/discharging test under various conditions. Battery efficiency can be calculated directly with the total heat involved during charging or discharging period. This information is very useful to battery researchers to gain insight into the battery chemistry within the cell and to understand battery performance.