HFM / GHP / tlr / TDW / GHFM
Heat Flow Meter / Guarded Hot Plate / Hot Box Test Chamber
Thermal conductivity and Thermal DiffusivityThermal diffusivity (a with the unit mm2/s) is a material-specific property for characterizing unsteady heat conduction. This value describes how quickly a material reacts to a change in temperature.thermal diffusivity are the most important thermophysical material parameters for the description of the heat transport properties of a material or component.
Based on an absolute measurement method, the GHP 456 Titan® is the ideal instrument for the determination of Thermal ConductivityThermal conductivity (λ with the unit W/(m•K)) describes the transport of energy – in the form of heat – through a body of mass as the result of a temperature gradient (see fig. 1). According to the second law of thermodynamics, heat always flows in the direction of the lower temperature.thermal conductivity of insulations.
The Thermal ConductivityThermal conductivity (λ with the unit W/(m•K)) describes the transport of energy – in the form of heat – through a body of mass as the result of a temperature gradient (see fig. 1). According to the second law of thermodynamics, heat always flows in the direction of the lower temperature.thermal conductivity as another significant thermophysical property is determined by means of heat flow meters (HFM) with the plate method for insulators.
NETZSCH instruments are based on the respective instrument and application standards for HFM (e.g. ASTM C518, ISO 8301, DIN EN 12667 EN 12, JIS A 1412, based on DIN EN 12664) and for GHP (ISO 8302, ASTM C177, DIN EN 12939, DIN EN 12667, DIN EN 13163).
Thermal conductivity and diffusivity are the most important thermophysical material parameters for the description of the heat transport properties of a material or component. Usually, Thermal ConductivityThermal conductivity (λ with the unit W/(m•K)) describes the transport of energy – in the form of heat – through a body of mass as the result of a temperature gradient (see fig. 1). According to the second law of thermodynamics, heat always flows in the direction of the lower temperature.thermal conductivity is determined by Heat Flow Meters (HFM) and Guarded Hot Plate (GHP).
For determining the Thermal ConductivityThermal conductivity (λ with the unit W/(m•K)) describes the transport of energy – in the form of heat – through a body of mass as the result of a temperature gradient (see fig. 1). According to the second law of thermodynamics, heat always flows in the direction of the lower temperature.thermal conductivity of pipe insulations NETZSCH offers the TLR 1000, a guarded hot pipe tester in accordance with DIN EN ISO 8497, DIN EN 1946-5, DIN 52613, ASTM C 534, and ASTM C 335.
The compact test chamber TDW 4040 is designed for testing brickwork in accordance with DIN EN 1934 (such as brick, lime sand brick, concrete, or aerated concrete), while TDW 4140 and TDW 4240 are designed for testing elements and components used in construction, such as windows, profiles, doors and domes. (Standards: DIN EN ISO 8990, DIN EN 1946-4, DIN EN ISO 12567, DIN EN 12412-2, ASTM C-1363)
method HFM
Heat Flow Meter (HFM)
based on ASTM C518, ASTM C1784, ISO 8301, JIS A1412, DIN EN 12664, and DIN EN 12667
In a heat flow meter (HFM), the test specimen is placed between two heated plates controlled to a user-defined mean sample temperature and temperature drop to measure heat flowing through the specimen. The sample thickness (L) corresponds to the actual sample dimension or to match the desired thickness of a compressible sample. The heat flow (Q) through the sample is measured by two calibrated heat flux transducers covering a large area of both sides of the specimen.
After reaching a thermal equilibrium, the test is done. The heat flux transducer output is calibrated with a standard. For the calculation of the Thermal ConductivityThermal conductivity (λ with the unit W/(m•K)) describes the transport of energy – in the form of heat – through a body of mass as the result of a temperature gradient (see fig. 1). According to the second law of thermodynamics, heat always flows in the direction of the lower temperature.thermal conductivity (λ) the average heat flux and the thermal resistance R is used, in accordance with Fourier’s Law (see formulas on the right). The thermal transmittance, also known as U-value, is the reciprocal of the total thermal resistance. The lower the U-value, the better the insulating ability.
method: GHP
Guarded Hot Plate (GHP)
based on well‐known, standardized guarded hot plate techniques, e.g., ISO 8302, ASTM C177 or DIN EN 12667
The Guarded Hot Plate instrument measures the thermal conductivity of insulation products.
The GHP principle is based on an absolute measurement method and therefore requires no calibration standards. It offers optimum accuracy in the available temperature range.
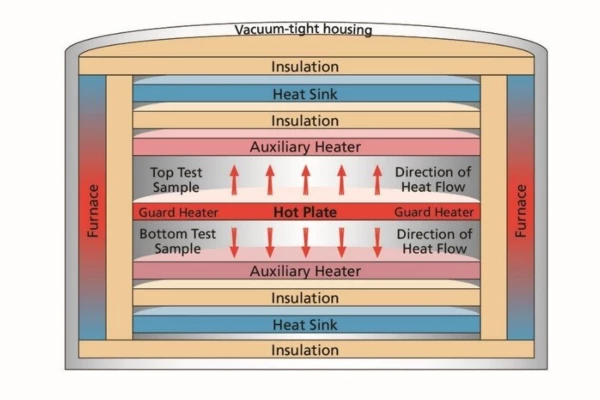
The hot plate and the guard ring are sandwiched between two specimens of the same material and approximately the same thickness (Δx). Typically, two specimens are preferred for a measurement, but it is also possible to work with only one test specimen.
Auxiliary heaters (cold plates) are placed above and below the samples. The cold plates are heated such that a precisely defined, user-selectable temperature difference (ΔT) is established between the hot and the cold plates and thus also over the entire sample thickness.
As soon as thermal equilibrium is reached, the power input in the hot plate with area A is measured.
The Absolute GHP Method
The great advantage of the GHP method is that it is an absolute method; i.e., no calibration or correction is required at all. The thermal conductivity values result in the stationary state simply from the:
- precisely measured total power input into the hot plate, Q,
- average sample thickness, d,
- measurement area, A, and
- mean temperature difference, ΔT, along the sample or the two samples, as the case may be (the factor 2 results for two samples):
The GHP method is described in, e.g., ISO 8302, ASTM C177 or DIN EN 12667. NETZSCH offers the GHP 456 Titan®®.
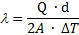
Application Literature

MEASUREMENT WANTED?
Our NETZSCH applications laboratory is providing contract testing services for a wide range of industries and research centers. It is equipped with state-of-the-art testing instruments allowing for a variety of thermal analysis measurements to be carried out.
Consult with the experts in our applications labs to choose the best-suited measuring method for your specific needs.