POLYMERS
Polymer Tape — Thermal Diffusivity
The LFA 447 NanoFlash® allows easy and fast temperature-dependent measurements of the Thermal DiffusivityThermal diffusivity (a with the unit mm2/s) is a material-specific property for characterizing unsteady heat conduction. This value describes how quickly a material reacts to a change in temperature.thermal diffusivity.
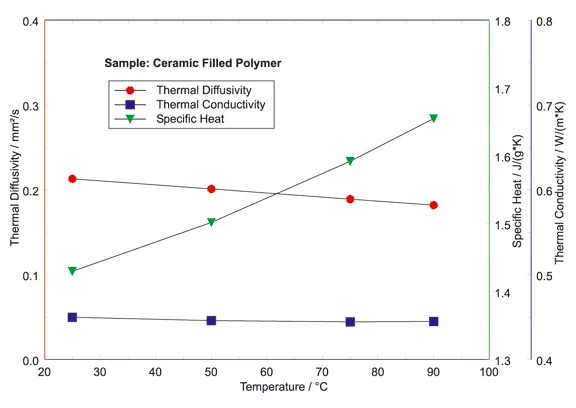
Additionally, the specific heat can be determined by employing a comparative method. A direct determination of the Thermal ConductivityThermal conductivity (λ with the unit W/(m•K)) describes the transport of energy – in the form of heat – through a body of mass as the result of a temperature gradient (see fig. 1). According to the second law of thermodynamics, heat always flows in the direction of the lower temperature.thermal conductivity is possible, if the bulk DensityThe mass density is defined as the ratio between mass and volume. density of the material is known. This method was used for the thermophysical properties characterization of a polymer tape between room temperature and 90°C. The calibration standard for the specific heat determination was Pyroceram 9606. It can clearly be seen that both the Thermal DiffusivityThermal diffusivity (a with the unit mm2/s) is a material-specific property for characterizing unsteady heat conduction. This value describes how quickly a material reacts to a change in temperature.thermal diffusivity and specific heat changed significantly versus temperature. The resulting Thermal ConductivityThermal conductivity (λ with the unit W/(m•K)) describes the transport of energy – in the form of heat – through a body of mass as the result of a temperature gradient (see fig. 1). According to the second law of thermodynamics, heat always flows in the direction of the lower temperature.thermal conductivity depicts nearly no temperature dependence.