Modulus of Rupture (MOR) of refractory ceramics up to 1500°C
The modulus of rupture (MOR) is an important variable in the characterization of refractory materials. Determination of the maximum load at high temperatures is a property which, along with other thermophysical properties, is an important parameter for quality control and development of furnace linings.
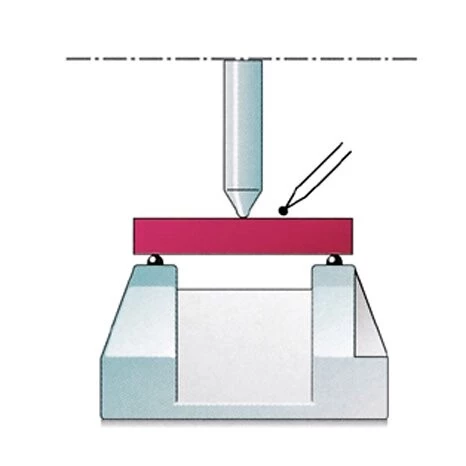
The modulus of rupture is defined as the maximum StressStress is defined as a level of force applied on a sample with a well-defined cross section. (Stress = force/area). Samples having a circular or rectangular cross section can be compressed or stretched. Elastic materials like rubber can be stretched up to 5 to 10 times their original length.stress a rectangular test piece of specific dimensions can withstand in a 3-point bending test until it breaks, expressed in N/mm2 or MPa.
The International Standard Test Method is described in ISO 5013; test piece dimensions: 150 mm x 25 mm x 25 mm.
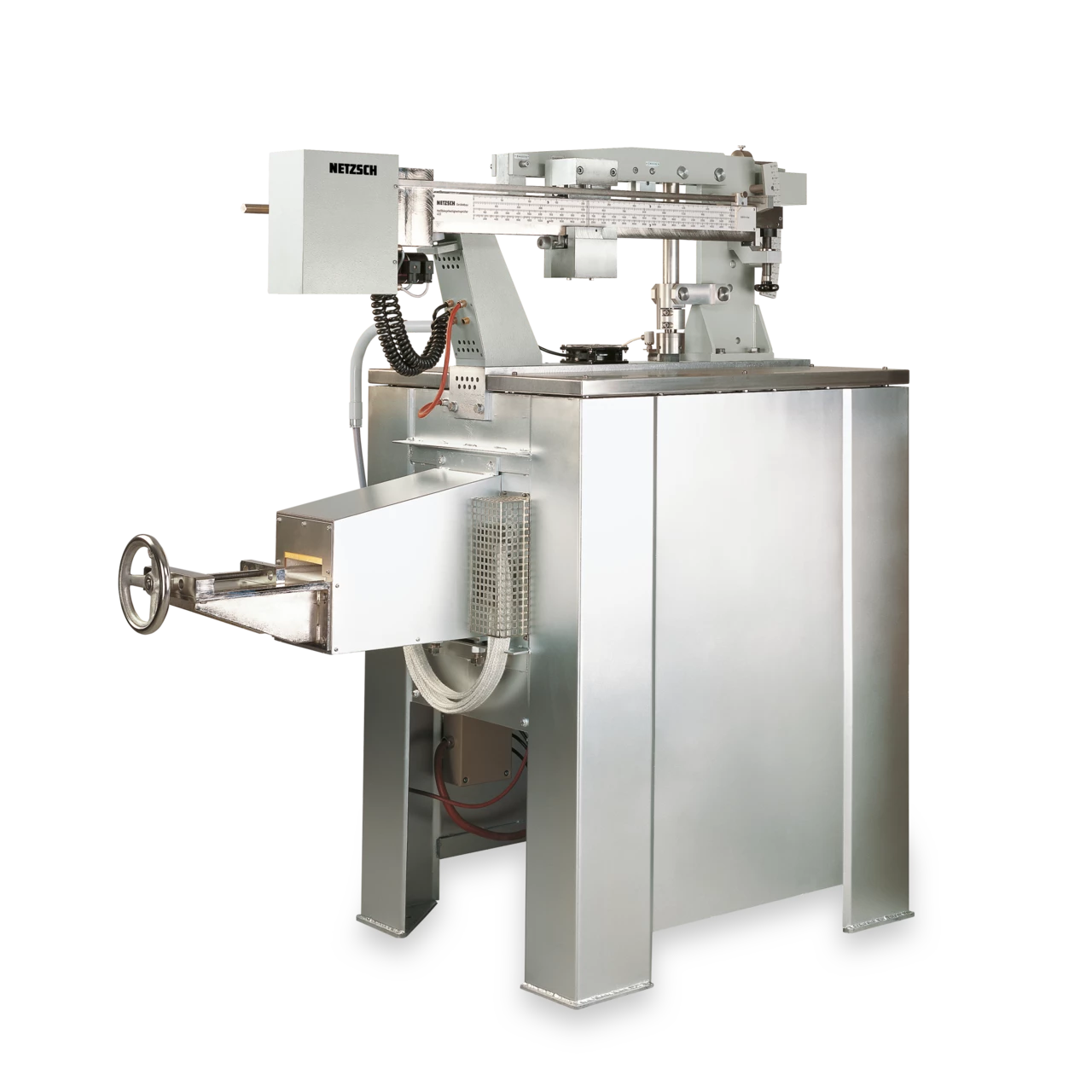
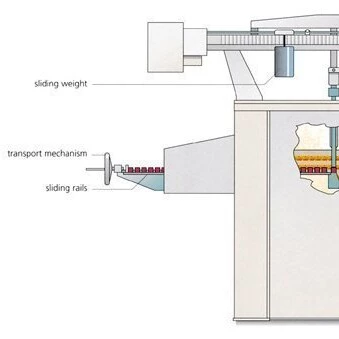
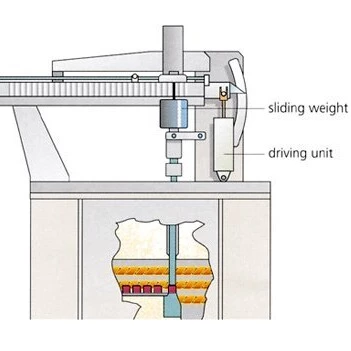
For determination of the modulus of rupture of refractories up to a temperature of 1500°C and a maximum load of 5000 N (60 N/mm2), NETZSCH offers the model 422 D/3. This model is designed for continuous testing with a 3-point bending device.
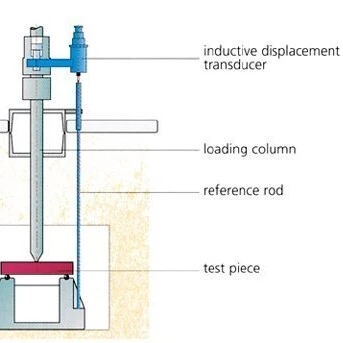
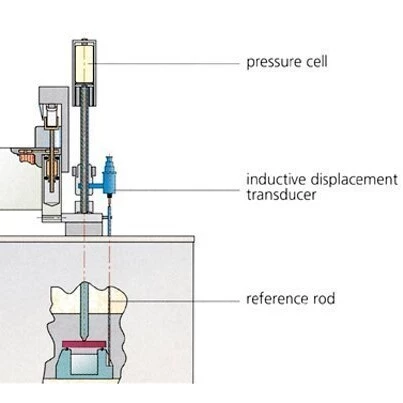
With optional devices for load and deformation measurement and/or constant deformation rate, additional information about the limits of elasticity and crack propagation in ceramic test pieces can be obtained.

Request a Quote
Technical Data
Heating elements
Bending measuring range
Temperature range
Bending support:
SiC
Load:
1 N to 5000 N
(2.0 to 12.5 N/s, switchable)
Temperature measurement:
type S thermocouples
Sample dimensions:
150 mm x 25 mm x 25 mm
Bending mode:
3-point
Atmospheres:
air, static