Glossary
Crystallinity / Degree of Crystallinity
Crystallinity refers to the degree of structural order of a solid. In a crystal, the arrangement of atoms or molecules is consistent and repetitive. Many materials such as glass ceramics and some polymers can be prepared in such a way as to produce a mixture of crystalline and amorphous regions.
However, even for completely crystalline materials, the degree of structural perfection can vary.
For example, most metallic alloys are crystalline, but usually comprise many independent crystalline regions (grains or crystallites).
In various orientations separated by grain boundaries, they also contain other crystallographic defects, such as dislocations. That reduces the degree of structural perfection.
The most highly perfect crystals are silicon boules produced for semiconductor electronics which are large single crystals (i.e., they have no grain boundaries); these are nearly free of dislocations and have precisely controlled concentrations of defect atoms.
CrystallizationCrystallization is the physical process of hardening during the formation and growth of crystals. During this process, heat of crystallization is released.Crystallization of polymers can be observed in some thermoplastics. When the melt solidifies, partial alignment of the molecular chains in the polymer occurs. Based on CrystallizationCrystallization is the physical process of hardening during the formation and growth of crystals. During this process, heat of crystallization is released.crystallization nuclei, the molecular chains fold together and form ordered regions called lamellae.

Do you have any questions?
Suitable products for your measurement
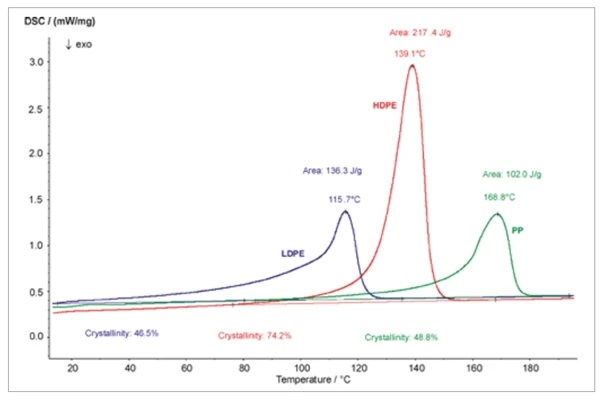
Degree of Crystallinity
The properties of plastics are significantly influenced by their degree of CrystallizationCrystallization is the physical process of hardening during the formation and growth of crystals. During this process, heat of crystallization is released.crystallization. The higher the degree of CrystallizationCrystallization is the physical process of hardening during the formation and growth of crystals. During this process, heat of crystallization is released.crystallization, the stiffer and stronger, but also more brittle a molded part is.
The degree of CrystallizationCrystallization is the physical process of hardening during the formation and growth of crystals. During this process, heat of crystallization is released.crystallization is influenced by the chemical structure and thermal history, such as the cooling conditions during processing or post-thermal treatment.
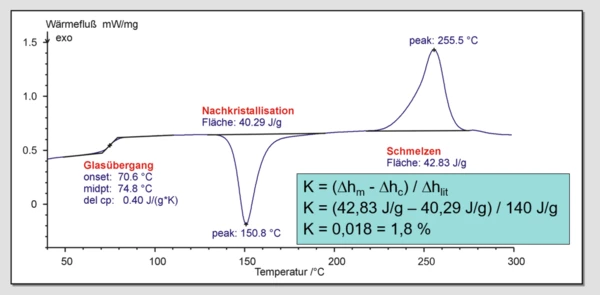
For determination of the degree of CrystallizationCrystallization is the physical process of hardening during the formation and growth of crystals. During this process, heat of crystallization is released.crystallization, K, the measured melting enthalpy ∆Hmeas is set in relation to the literature value ∆Hlit for completely crystalline material.
K= ∆Hmeas / ∆Hlit
Thermal history: The thermal or mechanical history is shown in the 1st heating curve of a DSC measurement. The 2nd heating curve serves for determination of the material properties under given dynamic conditions.
The degree of crystallinity has a significant influence on hardness, DensityThe mass density is defined as the ratio between mass and volume. density, transparency and diffusion.
However, the properties are not determined only by the degree of crystallinity, but also by the size of the structural units or the molecular orientation.