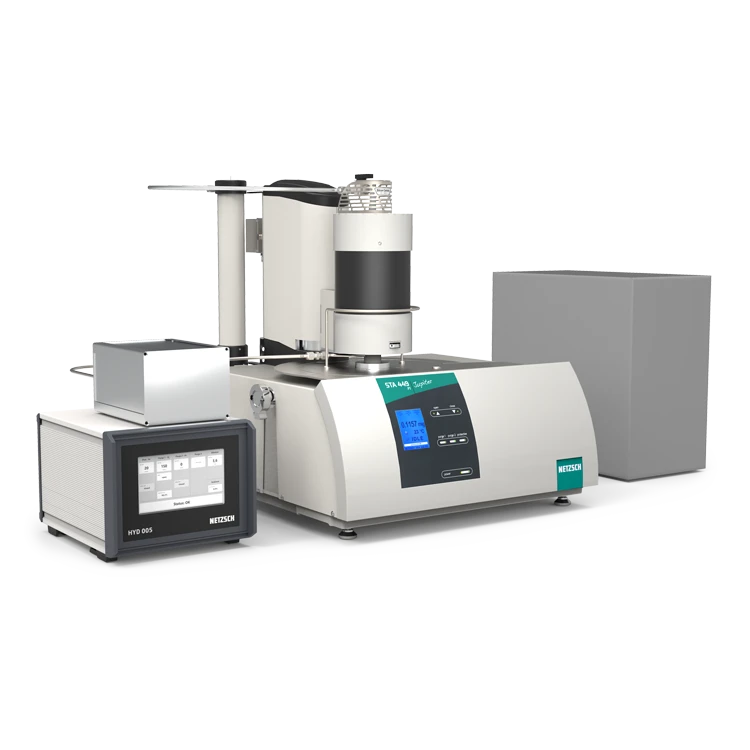
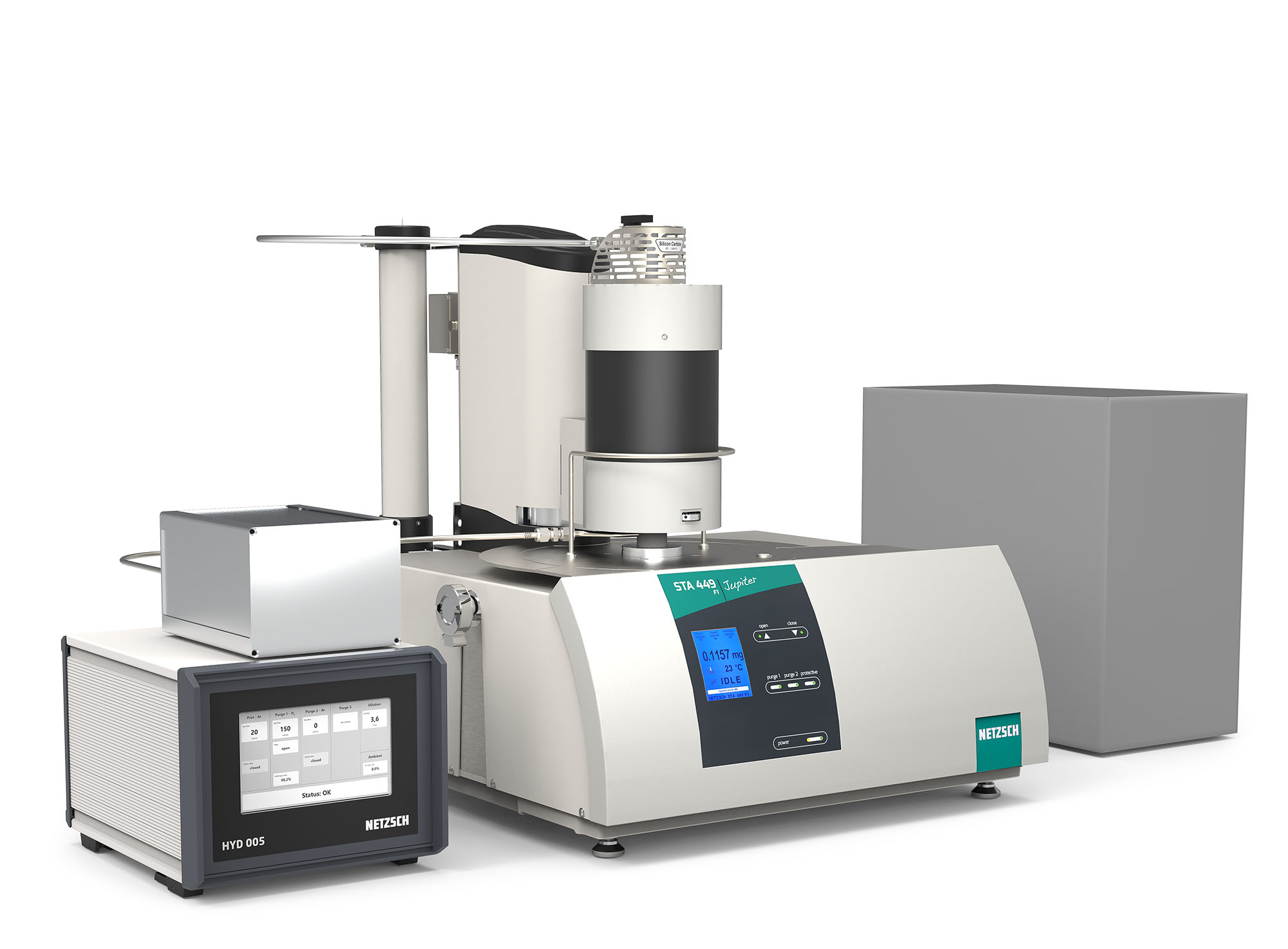
Thermal Analysis under Hydrogen
The Key to a Better Understanding of Material Interactions
Hydrogen (H2) is gaining attention for its potential role in sustainable practices and green technology. Research into the interaction of materials with hydrogen is critical for developing eco-friendly solutions that can significantly reduce environmental impact.
One notable application is the use of hydrogen to mitigate high CO2 emissions from metallurgical processes through direct reduction, such as in iron ore reduction. Chemical hydrogen storage, particularly through the use of metal hydrides, is another important avenue of research. Scientists are working to enhance volumetric and gravimetric capacities, as well as hydrogen adsorption/desorption kinetics and the life cycle of potential material candidates. Improving these aspects of materials can lead to more efficient and practical hydrogen storage solutions, which are vital for various applications including transportation, energy storage, and renewable energy systems.

Safe Measurements in Reducing or Oxidizing Atmospheres
The H2Secure concept developed by NETZSCH features a complete solution for conducting tests in environments with varying concentrations of hydrogen while providing utmost safety. This concept enables safe experimentation in a 100% H2 environment or with lower concentrations of H2 mixed with non-flammable gases such as nitrogen (N2) or argon (Ar) atmospheres. This flexibility is achieved through a comprehensive safety protocol embedded in the system.
One of the key features of the H2Secure concept is its ability to seamlessly perform complex OxidationOxidation can describe different processes in the context of thermal analysis.oxidation-reduction cycles. This involves switching between hydrogen- and oxygen-containing atmospheres within a single measurement, allowing for precise analysis of reaction kinetics and material behavior under different conditions. During these tests, it is crucial to maintain safety at all times. Therefore, in an intermediate state, the sample and testing apparatus are purged with inert gas. This purging process continues until safe conditions are reached for a gas change, minimizing any potential risks associated with handling hydrogen or oxygen.

Upgrade any STA 449
The H2Secure concept is readily accessible for any instrument of the STA 449 series, offering the flexibility of upgrading existing instruments. Upgraded instruments retain their complete functionality while also enabling safe operations with hydrogen. The upgrade encompasses all essential components and can be conveniently performed on-site by our service team.
Method
Simultaneous Thermogravimetry – Differential Scanning Calorimetry

The simultaneous application of Thermogravimetry (TGA) and Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) to a single sample in an STA instrument yields more information than separate application in two different instruments:
- The test conditions are perfectly identical for TGA and DSC signals (same atmosphere, flow rate, vapor pressure on the sample, heating rate, thermal contact to the sample crucible and sensor, radiation effect, etc.).
- The analyzability of the signals is improved, since two or more sets of information concerning sample behavior are always simultaneously available (differentiation between phase transformation and Reacción de DecomposiciónA decomposition reaction is a thermally induced reaction of a chemical compound forming solid and/or gaseous products. decomposition, between addition and condensation reactions, recognition of PyrolysisPyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of organic compounds in an inert atmosphere.pyrolysis, OxidationOxidation can describe different processes in the context of thermal analysis.oxidation, and combustion reactions, etc.).
- The Simultaneous Thermal Analysis (STA) method is exceptionally versatile, capable of accommodating complex experiments involving specialized atmospheric conditions such as water vapor, corrosive gases, and now, hydrogen atmospheres.
Simultaneous Thermal Analysis (STA) is based on standards, e.g., ISO 11358, ASTM E793, DIN 51004, DIN 51006, DIN 51007. It generally refers to the simultaneous application of Thermogravimetry (TGA) and Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) to one and the same sample in a single instrument.
H2Secure Concept
- The volume of H2 is precisely regulated by introducing hydrogen at the top of the furnace and confining it to a defined space above the continuously purged balance chamber.
- Gas concentrations of H2 and O2 are continuously measured for safe handling.
- The central communication unit, the H2Secure box, processes the overall information and controls the gas flows on the basis of pre-defined safety limits.
- Fail-safe operation is achieved by opening the magnetic valves in the event of a power failure, thus releasing an inert gas that removes the hydrogen from the system.
Set Up of the H2Secure Concept
Concept for the STA 449 Series
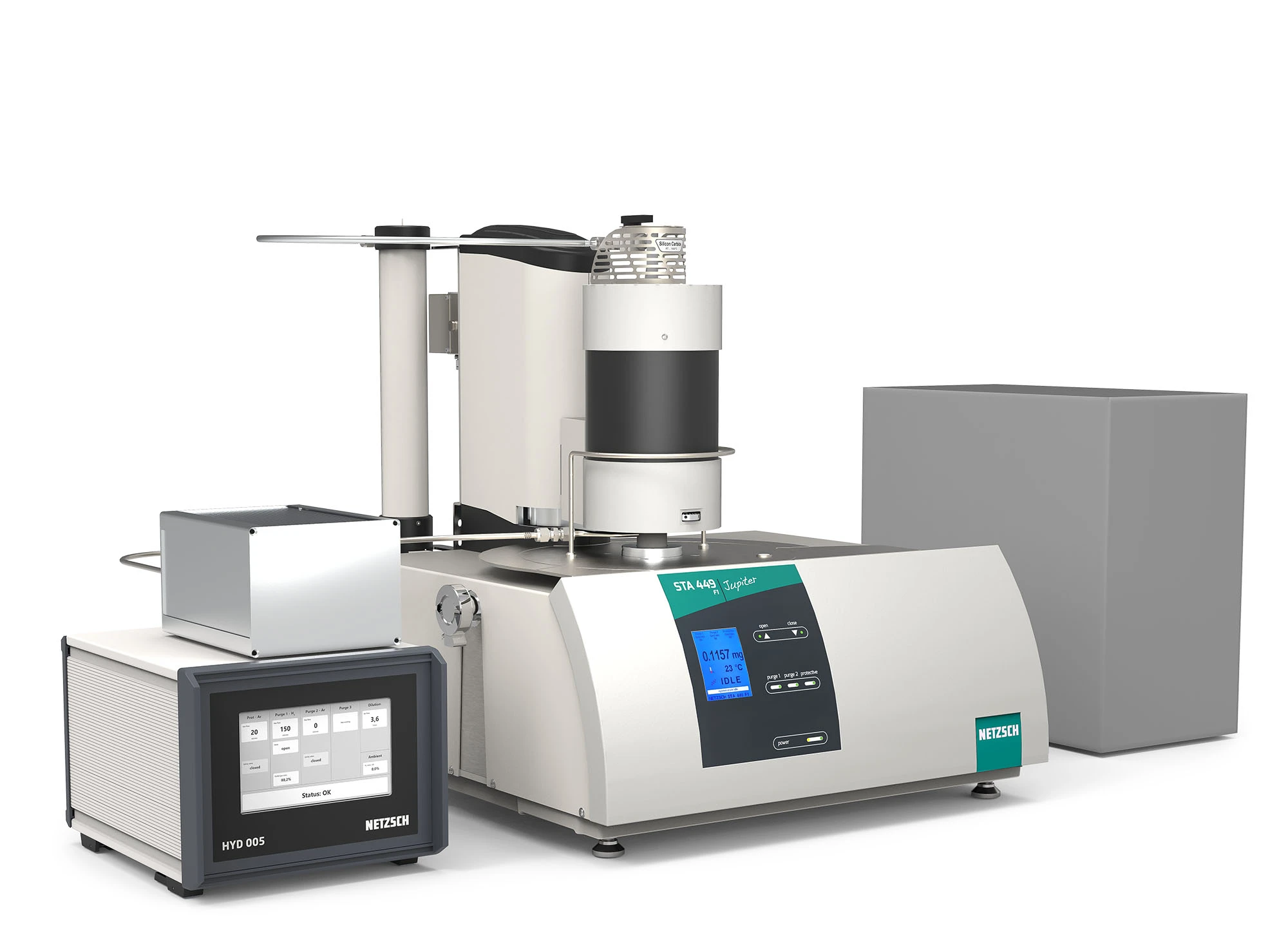

Specifications
| H2Secure for STA 449 | |
|---|---|
| Furnace type supporting H₂ measurements | SiC |
| Temperature range | RT to 1600°C |
| Sensor types* |
|
| Thermocouple types* |
|
| Sensor type for reduction experiments only | W |
| Optional 4-fold MFC | Possible switching between hydrogen and air atmospheres in one measurement |
| Hydrogen supply | Supplied by the operator, e.g., hydrogen generator, H₂ cylinder |
| H₂ and O₂ measuring cell | Included |
| H₂Secure Box | Included |
| Optional gas outlet treatment | H₂ dilution |
| Upgrade of existing STA 449 | Possible |
* Possibility of reduced life time depending on experimental parameters








