15.06.2023 by Aileen Sammler
Determination of Thermal Expansion: Common Sources of Error and how NETZSCH Dilatometers Can Minimize them
Dilatometry is an important method for measuring the change in length or volume of materials as it varies with temperature or other external influences. It is the method of choice for studying changes in length for ceramics, glasses, metals, composites and polymers as well as other structural materials. It allows for information to be obtained on thermal behavior, process parameters, and SinteringSintering is a production process for forming a mechanically strong body out of a ceramic or metallic powder. sintering (as well as crosslinking) kinetics.
Results obtainable by DIL measurements
- Linear thermal expansion
- Coefficient of thermal expansion (Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion (CLTE/CTE)The coefficient of linear thermal expansion (CLTE) describes the length change of a material as a function of the temperature.CTE)
- Volumetric change
- DensityThe mass density is defined as the ratio between mass and volume. Density change
- Shrinkage steps
- Softening point
- Glass transition temperature
- Anisotropic behavior
- Phase transitions
- SinteringSintering is a production process for forming a mechanically strong body out of a ceramic or metallic powder. Sintering temperature and step
- Influence of additives and raw materials
- Decomposition temperature of e.g. materials such as organic binders
- Optimizing of firing processes
- Caloric effects by using c-DTA
- Rate-Controlled Sintering (RCS)The properties of sintered products, such as density or particle size distribution, are determined by the sintering conditions (temperature, atmosphere, etc.) and especially by the sintering rates. Rate-Controlled Sintering (RCS)
- Kinetics Neo: Dilatometer measurements can be used for kinetic analysis, e.g. SinteringSintering is a production process for forming a mechanically strong body out of a ceramic or metallic powder. sintering. The NETZSCH Kinetics Neo software is available for this purpose).
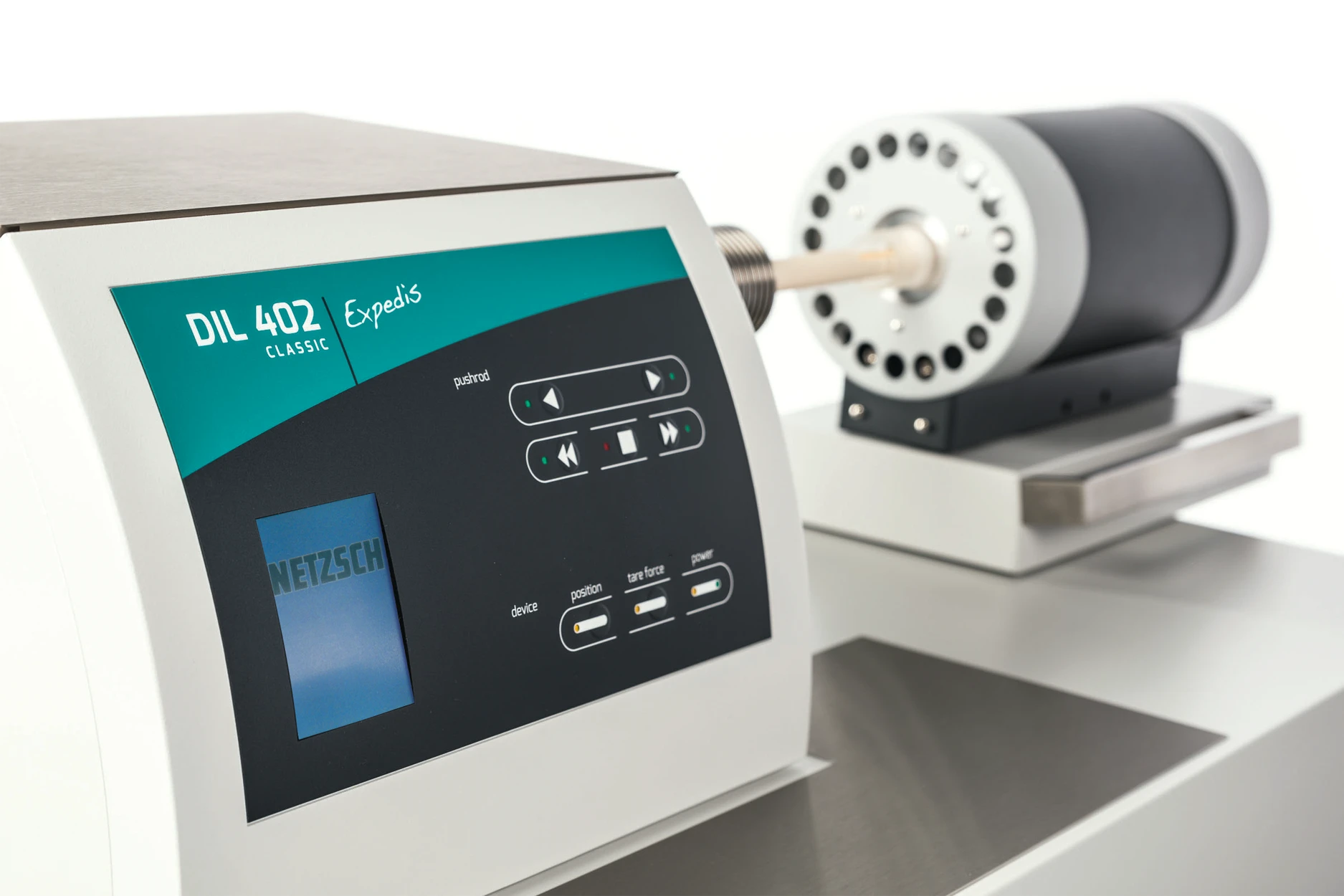

Sources of Error during Measurement and how to Minimize Them
When performing dilatometer measurements, however, various sources of error can occur that can lead to inaccurate results.
Here, we’ll present five common sources of error and explain why dilatometers (DIL) from NETZSCH Analyzing & Testing help minimize them.
- Sample preparation: Inadequate preparation of samples can lead to incorrect results. NETZSCH offers a wide range of accessories for its dilatometers, enabling specimens of various materials as well as different sizes and shapes to be well-prepared and measured: For example, we offer specimen grinders to produce plane-parallel samples, a special preparation set including a holder for foils, and special sample containers for powders and waxes to optimize your sample preparation.
For more information, please refer to our extensive accessories catalog. - Sample positioning: Incorrect positioning of the sample can lead to measurement errors. Dilatometers from NETZSCH have a MultiTouch function that “jiggles” the sample into the optimum position completely automatically and thus centers and aligns it correctly. In the process, the initial sample length is automatically determined at a predefined contact force.
- External temperature influences: Room temperature fluctuations can affect your measurement result, if the measuring system is insufficiently insulated. The measuring systems of our dilatometers are equipped with excellent insulation and, in the Select and Supreme version, also work with electronic temperature control to minimize these influences.
- Impurities: Impurities can also falsify the results. The robust robust sample holders and supports of the dilatometers by NETZSCH Analyzing & Testing can easily be cleaned thoroughly before measurement or replaced if necessary.
- Technical errors: Errors in the measuring device or the software can lead to incorrect results. NETZSCH dilatometers feature intelligent measuring systems, for example based on the interaction of an optoelectronic measuring sensor and the application of force that can be precisely controlled with the aid of an actuator. This enables a constant force to be applied regardless of the expansion or shrinkage of the sample between 10 mN and 3N: The NanoEye measuring system offers a high resolution of up to 0.1 nm over the entire measuring range of up to 50 mm, and does so maintenance-free with perfect linearity.
With the help of the integrated Proteus® dilatometer evaluation software, results can be determined reliably, quickly and easily.
Insert Text
NETZSCH dilatometers offer high precision, reliability and measuring accuracy in a temperature range from -180 up to 2800°C. The maintenance-free measuring system, automated measuring sequences and user-friendly Proteus® software enable simple and efficient operation and help minimize sources of error.
Learn more about our dilatometer product portfolio: Dilatometer (DIL) - NETZSCH Analyzing & Testing