Glossary
Crystallization Temperatures and Enthalpies
CrystallizationCrystallization is the physical process of hardening during the formation and growth of crystals. During this process, heat of crystallization is released.Crystallization is a naturally occurring or artificially initiated process for the solidification of substances or materials into a structured form, where the atoms or molecules are highly organized into a structure known as a crystal.
Some materials, such as drug substances in pharmaceuticals, can form several different crystal structures, called crystal modifications or crystal forms or polymorphs.
CrystallizationCrystallization is the physical process of hardening during the formation and growth of crystals. During this process, heat of crystallization is released.Crystallization occurs at a certain temperature and is accompanied by a certain amount of energy released (ExothermicA sample transition or a reaction is exothermic if heat is generated.exothermal process), which is known as the heat or enthalpy of CrystallizationCrystallization is the physical process of hardening during the formation and growth of crystals. During this process, heat of crystallization is released.crystallization. Furthermore, the CrystallizationCrystallization is the physical process of hardening during the formation and growth of crystals. During this process, heat of crystallization is released.crystallization procedure also has a kinetic component (rate of crystal growth), which should be taken into account in CrystallizationCrystallization is the physical process of hardening during the formation and growth of crystals. During this process, heat of crystallization is released.crystallization studies. CrystallizationCrystallization is the physical process of hardening during the formation and growth of crystals. During this process, heat of crystallization is released.Crystallization as a thermally initiated process often occurs in two major steps: The first step is nucleation, whereas the second step is known as crystal growth; the latter is also dependent upon the conditions of heat treatment.
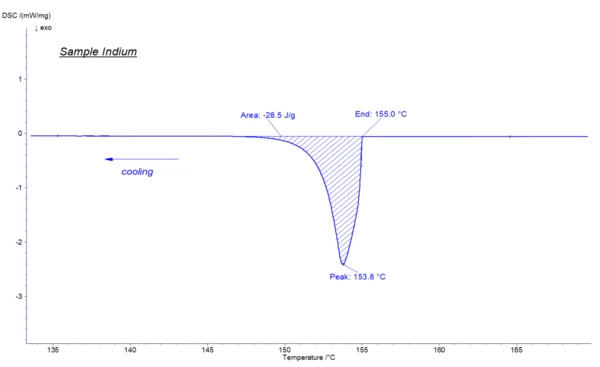
With the help of DSC (differential scanning calorimetry), the CrystallizationCrystallization is the physical process of hardening during the formation and growth of crystals. During this process, heat of crystallization is released.crystallization temperatures and the energy released can be determined with a high degree of reliability. It should be mentioned that the temperature at which CrystallizationCrystallization is the physical process of hardening during the formation and growth of crystals. During this process, heat of crystallization is released.crystallization takes place at DSC experiments might shift to lower temperature values due to cooling or super-cooling effects, which may occur during theCrystallizationCrystallization is the physical process of hardening during the formation and growth of crystals. During this process, heat of crystallization is released. crystallization process. In the below illustrated indium measurement, theCrystallizationCrystallization is the physical process of hardening during the formation and growth of crystals. During this process, heat of crystallization is released. crystallization occurred at 155°C, which is approximately 2 Kelvin lower than the Melting Temperatures and EnthalpiesThe enthalpy of fusion of a substance, also known as latent heat, is a measure of the energy input, typically heat, which is necessary to convert a substance from solid to liquid state. The melting point of a substance is the temperature at which it changes state from solid (crystalline) to liquid (isotropic melt).melting temperature of 156,6°C.
Besides the DSC method, dilatometry can also be applied to investigate such processes.