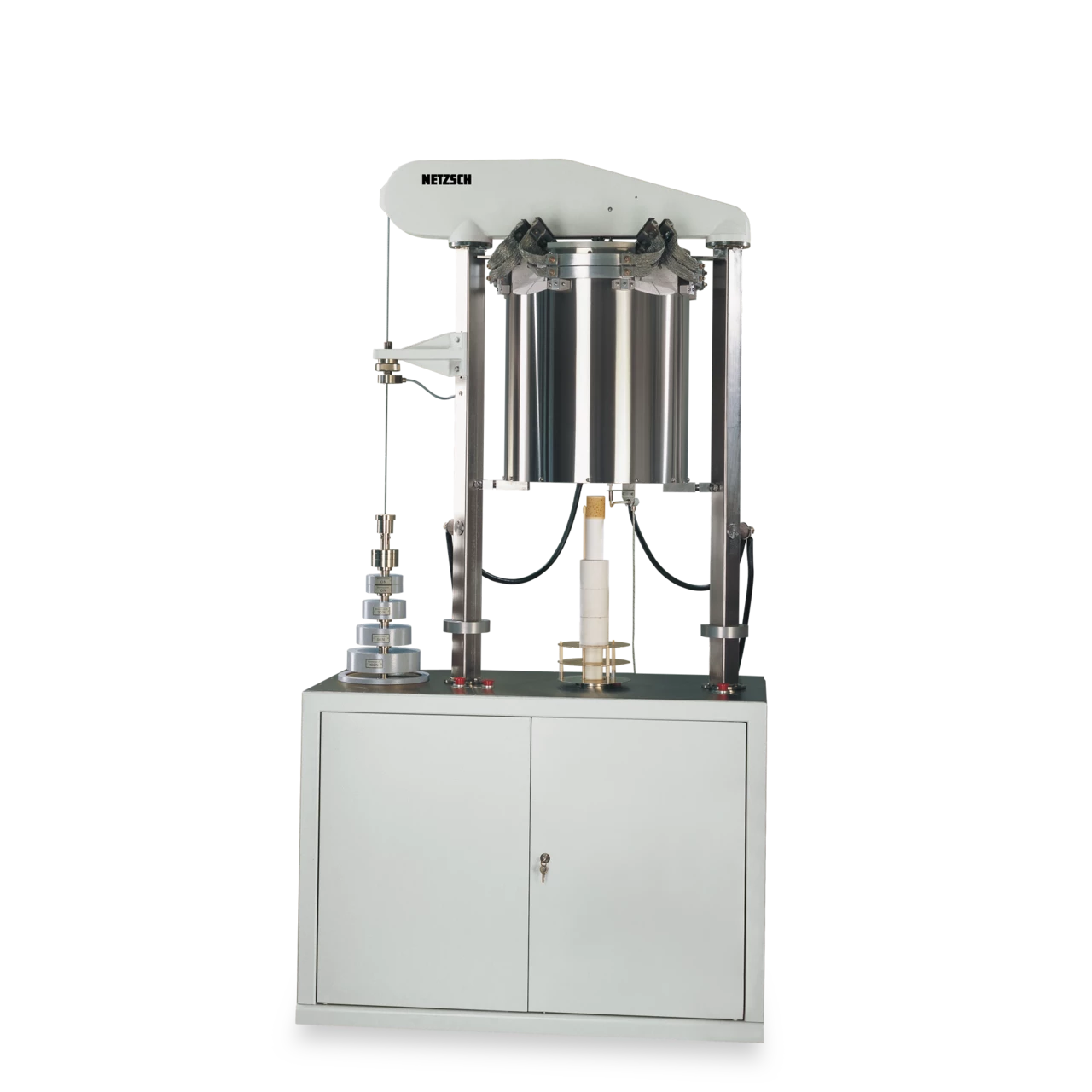
Determination of refractoriness under load (RUL) and CreepCreep describes a time and temperature dependent plastic deformation under a constant force. When a constant force is applied to a rubber compound, the initial deformation obtained due to the application of the force is not fixed. The deformation will increase with time.creep in compression (CIC) of refractory ceramics
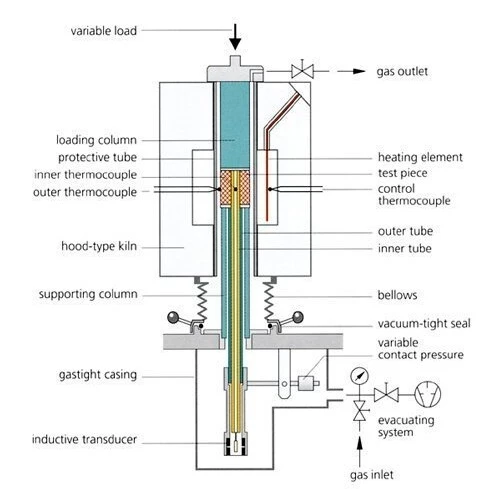
Refractoriness under load (RUL, according to ISO 1893) is a measure of the deformation behavior of refractory ceramic products subjected to a constant load and increasing temperature. The temperature range in which the softening occurs is not identical with the melting range of the pure raw material; however it must be reliably determined with the RUL 421 to check the use of refractory products in high-temperature applications.
CreepCreep describes a time and temperature dependent plastic deformation under a constant force. When a constant force is applied to a rubber compound, the initial deformation obtained due to the application of the force is not fixed. The deformation will increase with time.Creep in compression (CIC, according to ISO 3187) refers to the percent of shrinkage of a refractory test piece under a constant load and exposed to a constant high temperature over a long period of time. The CreepCreep describes a time and temperature dependent plastic deformation under a constant force. When a constant force is applied to a rubber compound, the initial deformation obtained due to the application of the force is not fixed. The deformation will increase with time.creep in compression test is also carried out in the RUL 421 to a maximum temperature of 1700°C. With its sturdy design, the RUL 421 is well suited for these long-running thermal and mechanical loads.
The same test-piece dimensions of 50 mm in diameter and 50 mm in height are used for both the RUL and the CIC tests. For the high-precision differential measuring system for determination of the deformation, the cylindrical test piece has a co-axial bore of 12.5 mm.
Selection and application of the load on the test piece are reproducible and independent of the deformation through use of the hood-type furnace with counterweights.
By reducing the load on the test piece to negligible values (as compared to the surface of the test piece), precise dilatometer measurements on large and even inhomogeneous samples can be carried out in the RUL 421 at temperatures up to 1700°C.

Request a Quote
Technical Data
Heating elements
Measuring range
Temperature range
Heating- and cooling rates:
0,01 K/min to 5 K/min
Sample holder:
Al2O3
Load:
1 N to 1000 N (in steps from 1 N to 100 N)
Δl resolution:
5 nm
Temperature measurement:
thermocouples (inner- and external temperature)
Sample length:
50 mm
Sample diameter:
50 mm
Atmospheres:
air, static (protective gas inlet optionally available)
Vacuumtight version
up to 10-2 mbar (special construction RUL/CIC 421 G)