Ceramici e Vetri
Matrice in allumina — Sinterizzazione
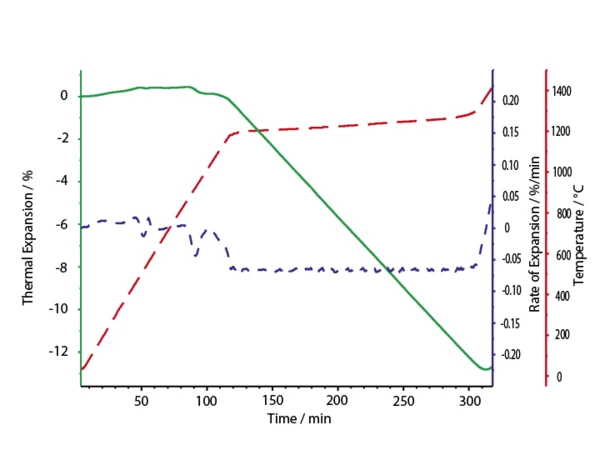
Una matrice in allumina è stata testata col DIL 402 C utilizzando il Software NETZSCH Rate-Controlled Sintering (RCS)The properties of sintered products, such as density or particle size distribution, are determined by the sintering conditions (temperature, atmosphere, etc.) and especially by the sintering rates. Rate Controlled Sintering (Rate-Controlled Sintering (RCS)The properties of sintered products, such as density or particle size distribution, are determined by the sintering conditions (temperature, atmosphere, etc.) and especially by the sintering rates. RCS).
La misura è stata eseguita con una velocità di riscaldamento di 10 K/min. E’ stata utilizzata la modalità start/stop del software Rate-Controlled Sintering (RCS)The properties of sintered products, such as density or particle size distribution, are determined by the sintering conditions (temperature, atmosphere, etc.) and especially by the sintering rates. RCS. Il valore di soglia era stabilito in 10 µm/min (0.046 %/min). La velocità di riscaldamento è stata ridotta dal software Rate-Controlled Sintering (RCS)The properties of sintered products, such as density or particle size distribution, are determined by the sintering conditions (temperature, atmosphere, etc.) and especially by the sintering rates. RCS durante la sinterizzazione per ottenere un costante tasso di contrazione. L’influenza degli additivi (es. legante organico, argille) è stata misurata sino a 1150°C. Lo step principale di sinterizzazione avviene tra 1150°C e 1350°C.