TMA
Analisi Termomeccanica (TMA)
Molti materiali subiscono variazioni delle proprie caratteristiche termomeccaniche durante un processo di riscaldamento o di raffreddamento. Ad esempio, le transizioni di fase, i processi di sinterizzazione o di rammollimento, possono essere concomitanti con l’espansione termica.
L’analisi TMA può quindi fornire delle informazioni rilevanti legate alla composizione, alla struttura, alle condizioni di produzione o alle possibilità applicative di numerosi materiali. L’impiego degli strumenti per analisi termomeccaniche si estende dal controllo-qualità alla ricerca e sviluppo. Settori tipici spaziano dalle materie plastiche in generale, ad elastomeri, vernici, materiali compositi, adesivi, film e fibre, materiali ceramici e vetrosi, fino ai metalli.
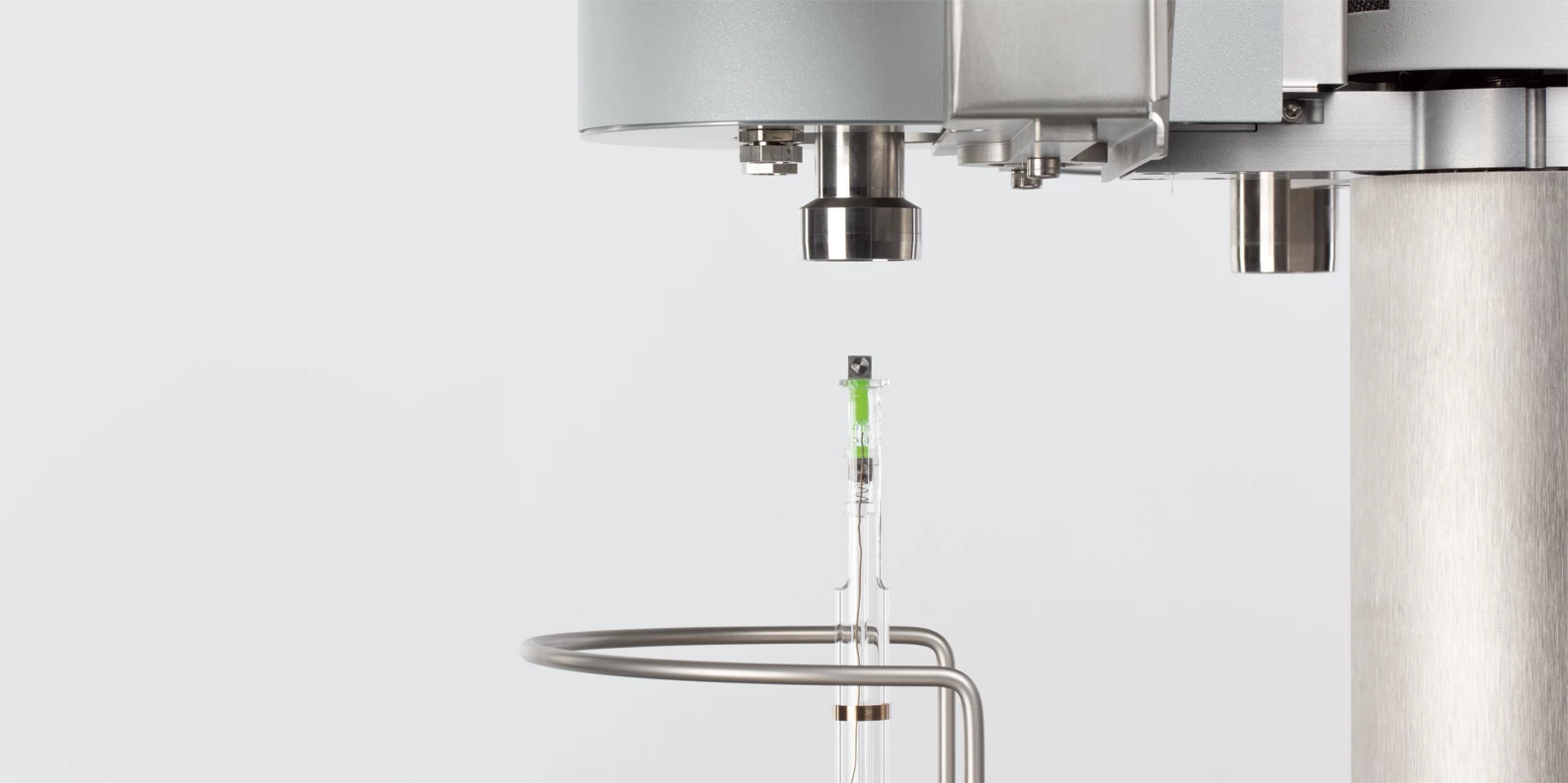
L’Analisi Termomeccanica consente di monitorare le variazioni dimensionali di solidi, liquidi e paste in funzione della temperatura o del tempo e sotto l’effetto di una forza meccanica (DIN 51 005, ASTM E831, ASTM D696, ASTM D3386, ISO 11359 Parti 1-3). È una tecnica strettamente legata alla dilatometria (dilatometro verticale), che misura le variazioni di lunghezza dei campioni, ma sotto un carico trascurabile (p. e. DIN 51 045).
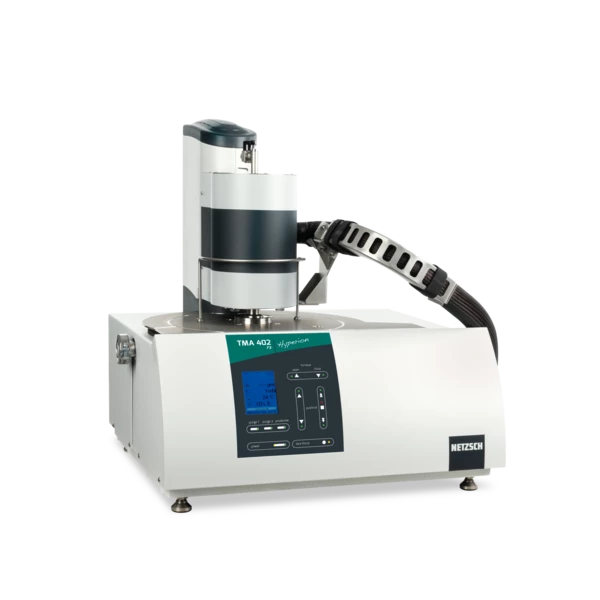
TMA 402 F3 Hyperion® Polymer Edition
Thermomechanical Analysis – TMA - Tailor-Made for Low-Temperature Applications
Polymers undergo changes in their thermomechanical properties during heating and cooling. TMA analyses can give insights into molecular orientation and quenching effects during cooling. It allows the design of adhesives and other hybrid joints and quality control of shrink films.
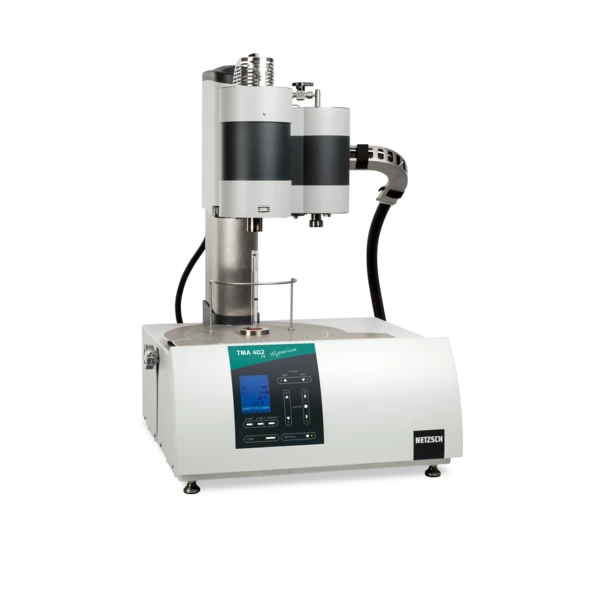
TMA 402 F1 /F3 Hyperion®
Thermomechanical Analyzer - Vertical Dilatometer
Modular Concept with interchangeable furnaces (compatible with other NETZSCH instruments) for easy and cost-effective expansion and retrofitting.Gas flows with up to 4 MFCs, controllable via software with programmable atmosphere change for the analysis of e.g. OxidationOxidation can describe different processes in the context of thermal analysis.Oxidation behavior without manual valve operation
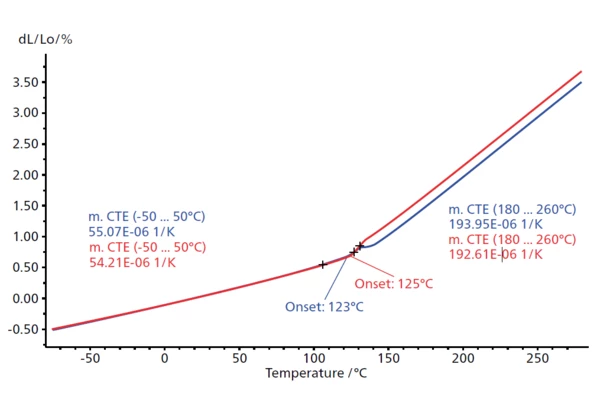
Thermal Expansion
The linear thermal expansion is an important variable for assessing the dimensional behavior of a material in response to a change in temperature.
This plot shows the thermal expansion (dL/L0 in %) of an epoxy resin between -70°C and 270°C. In the first heating (blue curve), the onset of the Temperatura di transizione vetrosaLa transizione vetrosa è una delle più importanti proprietà chimico-fisiche dei materiali amorfi e semi-cristallini, come, ad esempio, vetri, metalli (amorfi), polimeri, ingredienti farmaceutici e alimentari e definisce l’intervallo di temperatura in cui le proprietà meccaniche die materiali variano da duro e fragile a più morbido, malleabile o gommoso.glass transition (Tg) occurs at 123°C. In the second heating (red curve), the onset of Tg is slightly shifted, to 125°C. This shift could be due to RelaxationWhen a constant strain is applied to a rubber compound, the force necessary to maintain that strain is not constant but decreases with time; this behavior is known as stress relaxation. The process responsible for stress relaxation can be physical or chemical, and under normal conditions, both will occur at the same time. relaxation effects or post-curing.
Letteratura applicativa

MEASUREMENT WANTED?
Our NETZSCH applications laboratory is providing contract testing services for a wide range of industries and research centers. It is equipped with state-of-the-art testing instruments allowing for a variety of thermal analysis measurements to be carried out.
Consult with the experts in our applications labs to choose the best-suited measuring method for your specific needs.







