Introduction
Nowadays, biomass is more and more frequently used as an alternative to conventional energy sources. Key benefit is the “CO2 neutrality“. Wood belongs to the most important renewable raw materials. The main components of wood are cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin.
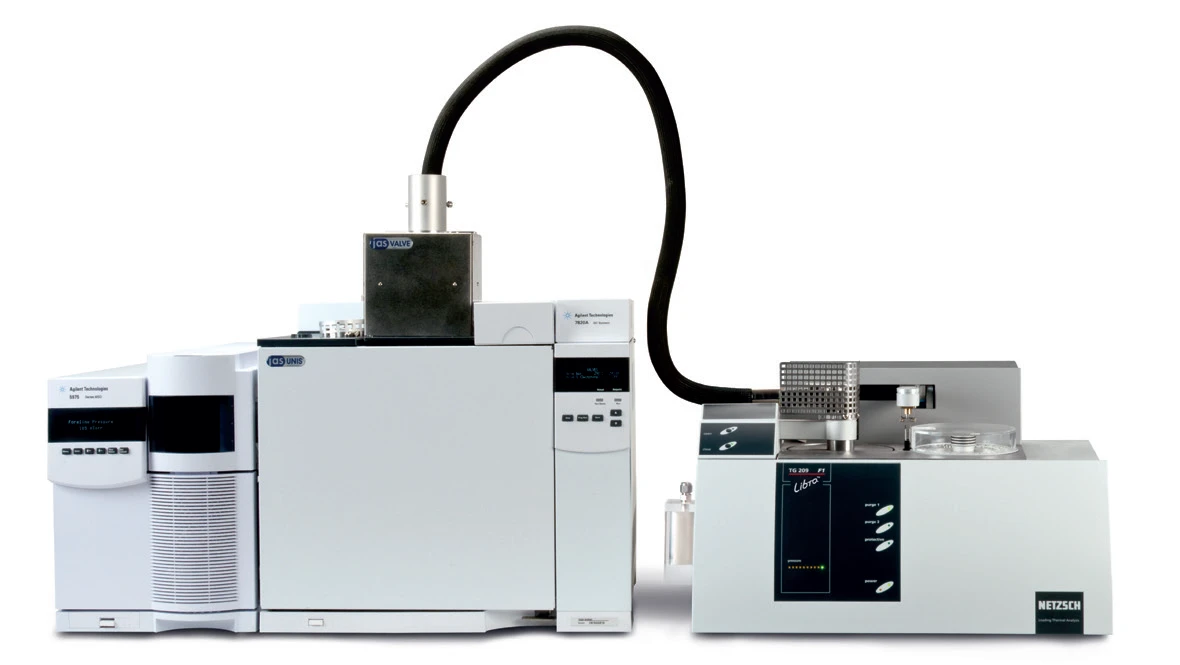

Table 1: TGA measurement parameters
Parameters
| Temperature range | RT to 500°C |
|---|---|
| Heating rate | 10 K/min |
| Atmosphere | Helium |
| Flow rate | 65 ml/min |
| Sample holder | Sample holder for corrosive gases |
| Crucible | Al2O3 (85 μl) |
| Sample mass | 6.9 mg |
Table 2: GC-MS measurement parameters
| Parameters | Quasi-continuous Mode | Event-controlled Mode |
|---|---|---|
| Column | Agilent HP-5ms | Agilent HP-5ms |
| Column length | 30 m | 30 m |
| Column diameter | 0.25 mm | 0.25 mm |
| Furnace temperature | 150°C | 100°C to 310°C (10 K/min) |
| Gas | Helium | Helium |
| Gas flow (split) | 20 ml/min (10:1) | 20 ml/min (10:1) |
| Column flow | 2 ml/min | 2 ml/min |
| Valve | every 2 min | 1x per event |
Quasi-continuous Mode
Simultaneous coupling of the TGA to the GC-MS allows for easy correlation of the outgassing substances with temperature.
The PyrolysisPyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of organic compounds in an inert atmosphere.pyrolysis of pinewood takes place in three steps (figure 2). The first step is the evolvement of the water contained. The main Decomposition reactionA decomposition reaction is a thermally induced reaction of a chemical compound forming solid and/or gaseous products. decomposition of wood occurs at approx 300°C.
First, the cellulose components are decomposed, then the lignin components decompose.
Corresponding to the DTG curve, the main Decomposition reactionA decomposition reaction is a thermally induced reaction of a chemical compound forming solid and/or gaseous products. decomposition can be seen at 300°C in the total ion chromatogram.
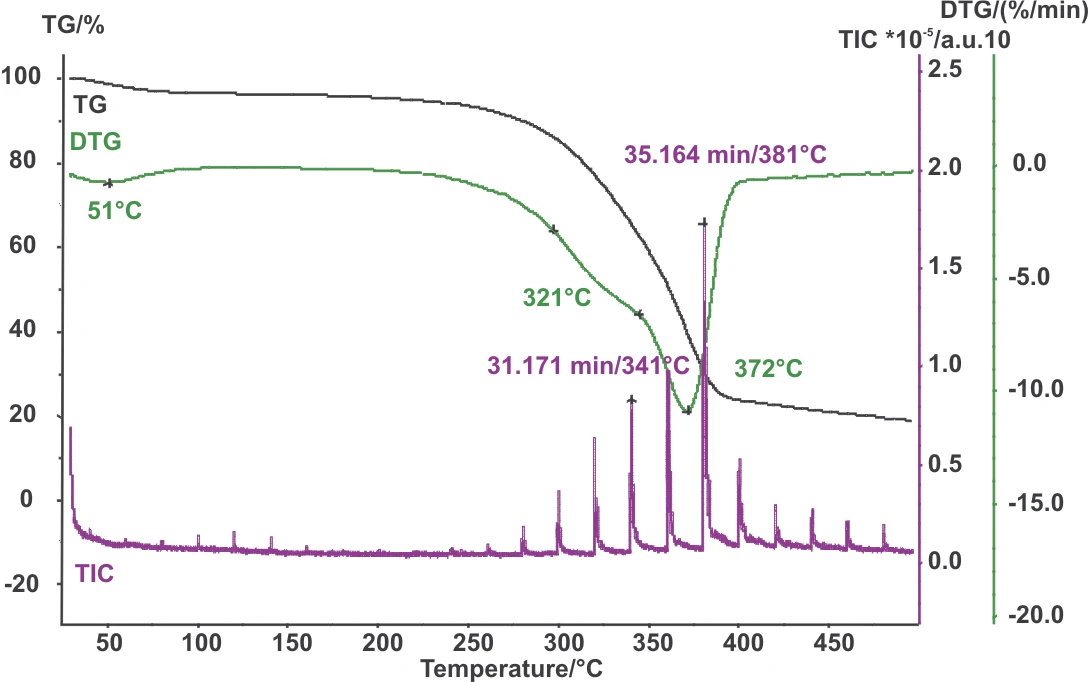
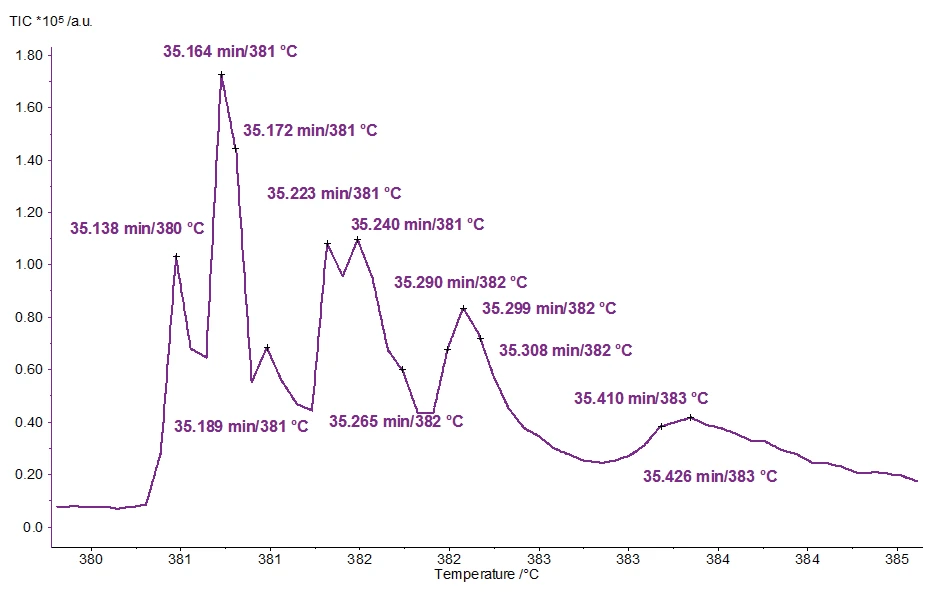
An enlarged scaling of the TIC in this range is presented in figure 3; the substances detected at the peaks are listed in table 3.
Table 3: Detected molecules and their retention times
| Time/Min | Molecule | Molar Mass | Mass Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| 35.138 | Acetone | 58 | 58 |
| 35.164 | 1,2,3-Thiadiazole | 86 | 58, 86 |
| 35.172 | 2-Methylfuran | 82 | 82, 81, 53 |
| 35.189 | 2-Methyl-Mannomethylpyranosid | 178 | 60, 74 |
| 35.223 | 2-Butenal, 2-Methyl | 84 | 55, 84 |
| 35.240 | Thiophene | 84 | 84, 58, 45 |
| 35.265 | Furan, 2,3-Dihydro-5-Methyl | 84 | 84, 55, 69 |
| 35.290 | Furfural | 96 | 96, 95 |
| 35.299 | 1H-Pyrazol, 1,3-Dimethyl | 96 | 96, 81, 68, 54 |
| 35.308 | 2,5-Dimethylfuran | 96 | 96, 95, 81, 53 |
| 35.409 | 2(5H)-Furanon | 84 | 55, 84, 70 |
| 35.426 | 2H-Pyran, 3,4-Dihydro | 84 | 55, 84, 69 |
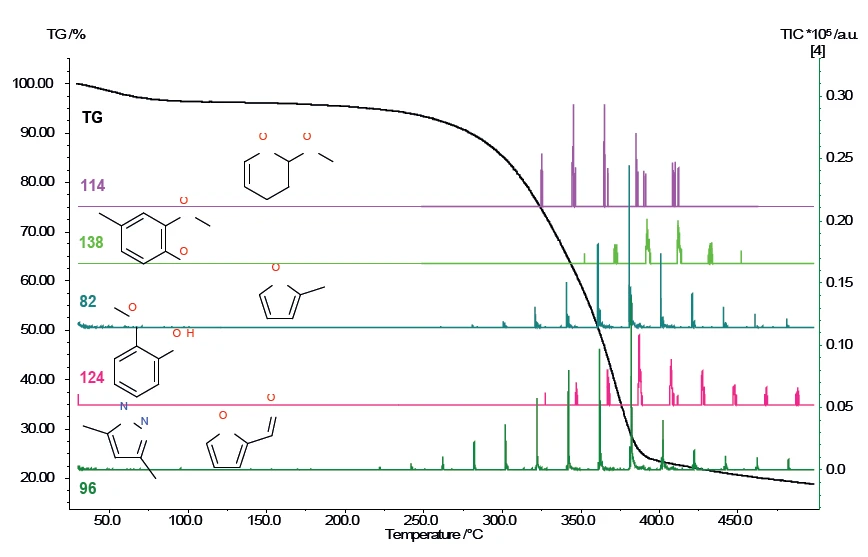
The individual mass numbers for pinewood are presented in figure 4 as a function of temperature.
Event-controlled Mode
For a more detailed evaluation of the forming substances, the TGA-GC-MS measurement was carried out in the event-controlled mode (figure 5). For this, individual chromatograms at certain temperatures were recorded.
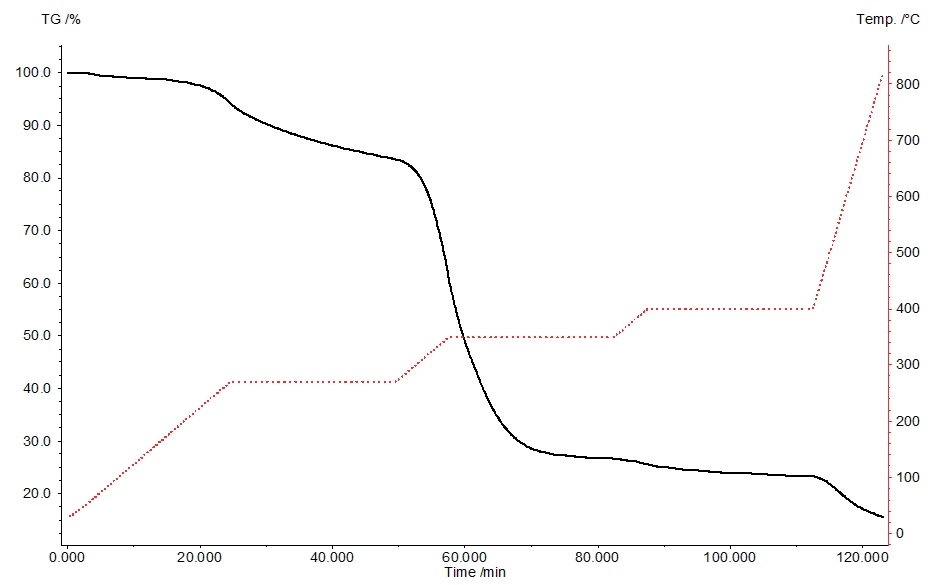
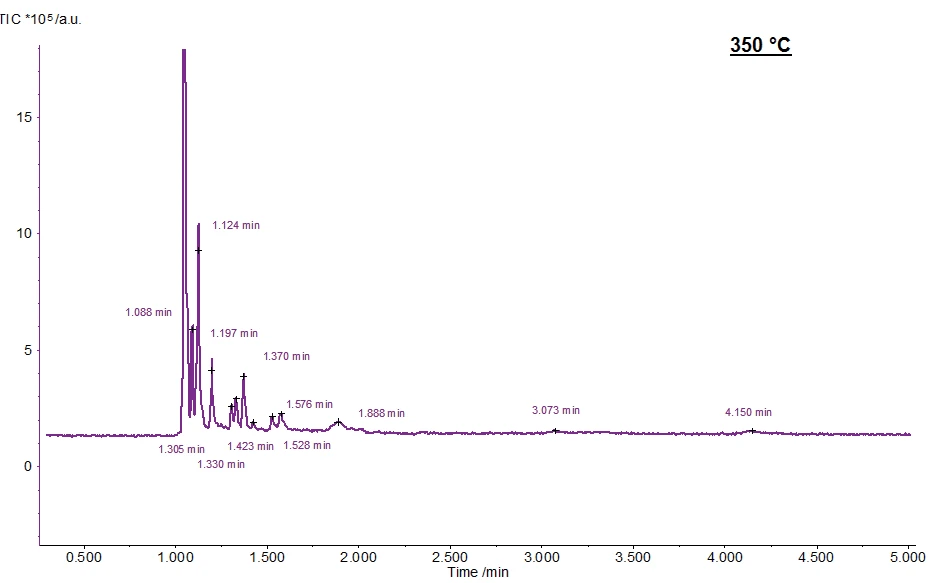
Figure 6 shows the chromatogram at 350 °C. The substances measured at the corresponding retention times are presented in table 4.
Table 4: Detected molecules at 350°C and their retention times
Parameters
| Retention time/min | Substance |
|---|---|
| 1.047 | CO2 |
| 1.088 | 3(2H)-Furanon, Dihydro-2-Methyl |
| 1.124 | 1-Propanol |
| 1.197 | 1-Hydroxy-2-Propanone |
| 1.305 | 2(5H)-Furanon |
| 1.330 | Acetic Acid, Methylester |
| 1.370 | Acetone |
| 1.424 | 4H-1,2,4-Tiazol, 4-Amino |
| 1.528 | Fufural |
| 1.576 | 2-Furanmethanol |
| 1.888 | 2(3H)-Furanon, 5-Methyl |
| 3.073 | Phenol, 2-Methoxy |
| 4.150 | Phenol, 2-Methyoxy-4-Methyl |