batteries
Manganese Oxide — Reduction
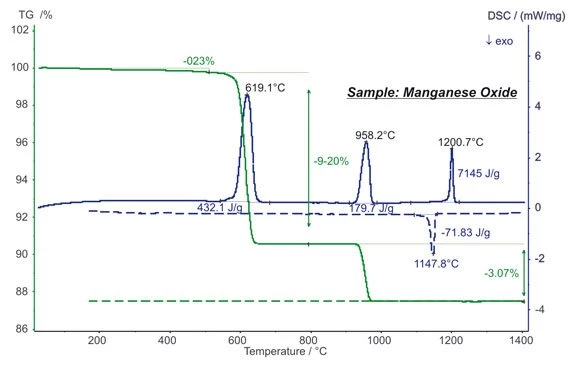
Manganese oxide (MnO2) is often used in chemistry as an oxidizer but also, for example, as a cathode material in batteries.
The STA measurement shows mass steps at approx. 600°C and 950°C which are due to the reduction of MnO2 into Mn2O3 and finally into Mn3O4. The values of 9.20% and 3.07% match exactly with the stoichiometrical values thus reflecting the high accuracy of the balance system. EndothermicA sample transition or a reaction is endothermic if heat is needed for the conversion.Endothermic DSC peaks with enthalpies of 432 J/g and 180 J/g were detected during the reduction steps. The EndothermicA sample transition or a reaction is endothermic if heat is needed for the conversion.endothermic DSC peak at 1200°C is due to a reversible structural transformation, which is observed at 1148°C upon cooling also as ExothermicA sample transition or a reaction is exothermic if heat is generated.exothermal peak (dashed lines). (measurement with STA 449 F1 Jupiter®®)