DSC/DTA
Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) / Differential Thermal Analysis (DTA)
Thanks to its versatility and explanatory power, Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) is the most-employed Thermal Analysis method.
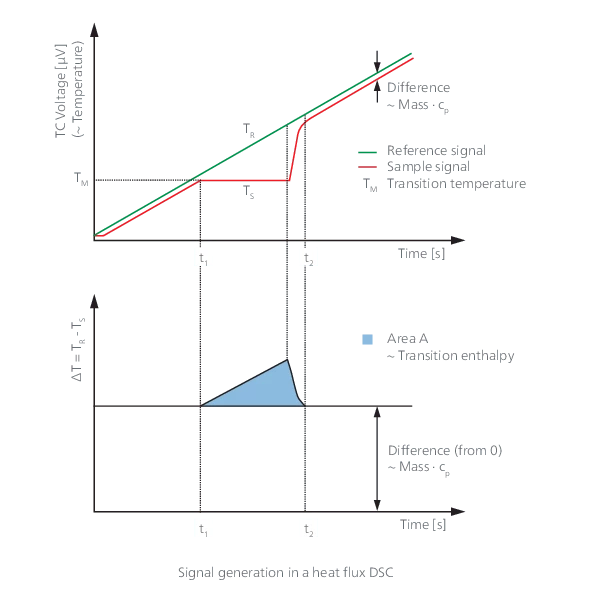
As per ISO 11357-1 with this method, a sample and a reference are subjected to a controlled temperature program (heating, cooling or IsothermalTests at controlled and constant temperature are called isothermal.isothermal). The actual measured properties are the temperature of the sample and the temperature difference between sample and reference. From the raw data signals, the heat flow difference between sample and reference can be determined.
NETZSCH DSC instruments work according to the heat flow principle and are characterized by a three-dimensional symmetrical construction with homogeneous heating. Sensors with high calorimetric sensitivity, short time constants and a condensation-free sample chamber in the calorimeter cell guarantee high detection sensitivity and stable, reproducible baselines over the entire life cycle of a calorimeter: ideal qualifications for successful application in research and academia, materials development and quality control.
Of course, our Differential Scanning Calorimeters (DSC) meet the respective instrument and application standards, including: ISO 11357, ASTM E967, ASTM E968, ASTM E793, ASTM D3895, ASTM D3417, ASTM D3418, DIN 51004, DIN 51007, DIN 53765.
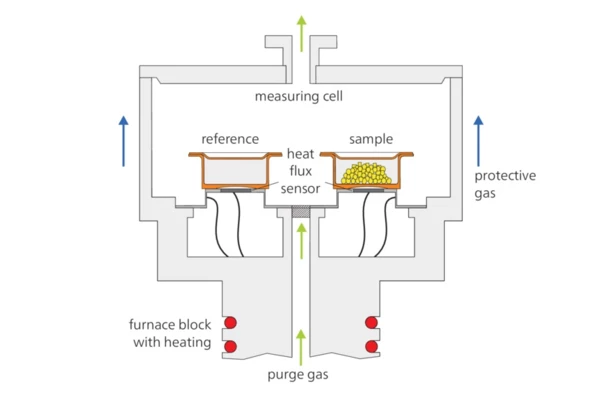
The DSC systems are based on relevant instrument and application standards, e.g., ISO 11357, ASTM E793, ASTM D3895, ASTM D3417, ASTM D3418, DIN 51004, DIN 51007.
Application Literature

MEASUREMENT WANTED?
Our NETZSCH applications laboratory is providing contract testing services for a wide range of industries and research centers. It is equipped with state-of-the-art testing instruments allowing for a variety of thermal analysis measurements to be carried out.
Consult with the experts in our applications labs to choose the best-suited measuring method for your specific needs.