Introduction
Thermogravimetry (TG) or thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) – as per ISO 11358 or DIN 51006, for example – allows for investigating the Thermal StabilityA material is thermally stable if it does not decompose under the influence of temperature. One way to determine the thermal stability of a substance is to use a TGA (thermogravimetric analyzer). thermal stability and composition of a variety of substances, materials and mixtures by heating the sample in a thermobalance under defined conditions. The surrounding atmosphere plays an important role here, so the primary focus lies on effects caused by interaction of the sample with its environment – i.e., adsorption, desorption, Decomposition reactionA decomposition reaction is a thermally induced reaction of a chemical compound forming solid and/or gaseous products. decomposition and OxidationOxidation can describe different processes in the context of thermal analysis.oxidation processes.
Under inert pyrolytic conditions (e.g., in a nitrogen atmosphere), for example, the results obtained differ radically from those obtained under oxidative conditions – i.e., in the presence of air or oxygen.
Measurement Results
Influence of the Atmosphere
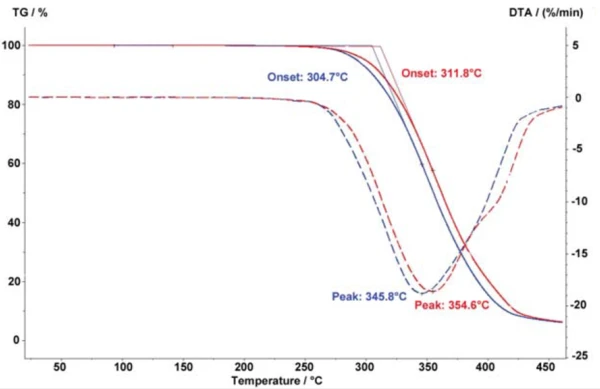
Figure 1 compares the Decomposition reactionA decomposition reaction is a thermally induced reaction of a chemical compound forming solid and/or gaseous products. decomposition of the thermoplastic elastomer blend SEBS/PP (styrene-ethylene-butadienestyrene/ polypropylene) in a nitrogen atmosphere (green curves) to the same measurement in air (blue curves). Decomposition reactionA decomposition reaction is a thermally induced reaction of a chemical compound forming solid and/or gaseous products. Decomposition of the OxidationOxidation can describe different processes in the context of thermal analysis.oxidation-sensitive material clearly begins much earlier in air: 312°C as compared to 391°C (extrapolated onset) under an inert gas atmosphere. In addition, the oxidative Decomposition reactionA decomposition reaction is a thermally induced reaction of a chemical compound forming solid and/or gaseous products. decomposition occurs in multiple steps, which can clearly be seen in the 1st derivative. In both cases, the heating rate was 20 K/min and the sample mass was 10 mg.
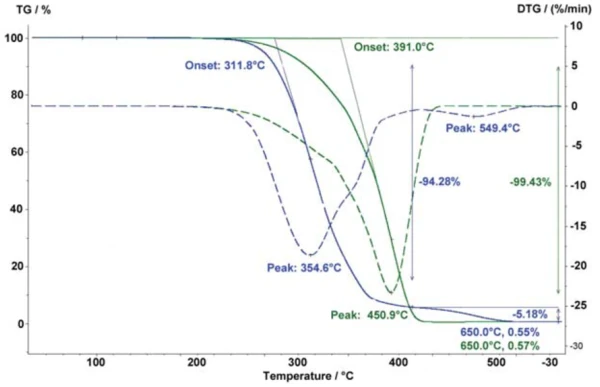
Under reduced atmospheric pressure – i.e., in a vacuum – the boiling point of volatile components in a polymer mixture can be lowered, thereby allowing for a better separation from the polymer Decomposition reactionA decomposition reaction is a thermally induced reaction of a chemical compound forming solid and/or gaseous products. decomposition. Figure 2 shows measurements on a mixture of the thermoplastic elastomer SEBS with a low-molecular plasticizer. Under vacuum (red curves), the separation of the plasticizer occurs at a considerably lower temperature. It is thereby possible to determine the exact plasticizer content, which is here 61.2%. In a nitrogen atmosphere, the decomposition process is partially overlapped by the polymer decomposition; the DTG curve (blue dotted line) does not return to 0. A heating rate of 5 K/min was employed in both cases.
Influence of the Sample Shape: Surface-to-Mass Ratio
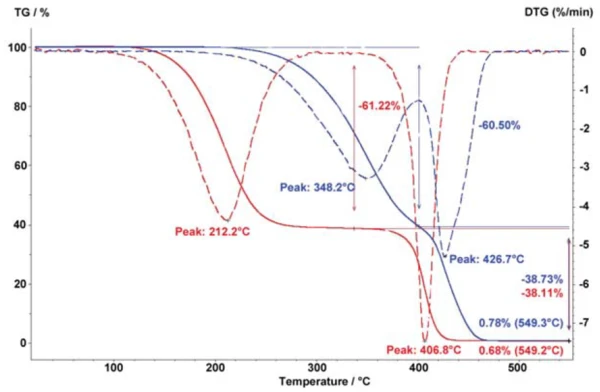
In decomposition analysis, the surface-to-mass ratio is also important for obtaining a reproducible measurement result. With a higher specific surface (e.g., as with powders), decomposition takes place at considerably lower temperatures and with steeper mass-loss steps than it would in bulk material of the same mass. The surface-to-mass ratio also influences the decomposition process for polymer samples, which might be available either as compact samples or cut into small pieces. Figure 3 shows the different decomposition behavior between an SEBS/PP sample which is cut into pieces (blue curves) – and therefore has a higher specific surface – as compared to a bulk sample (red curves) with an identical sample mass of 10 mg.