Pharma
Phenacetin and
p-Aminobenzoic acid — Purity
A eutectic system is an homogeneous mixture of 2 components that melts and solidifies like a pure substance.
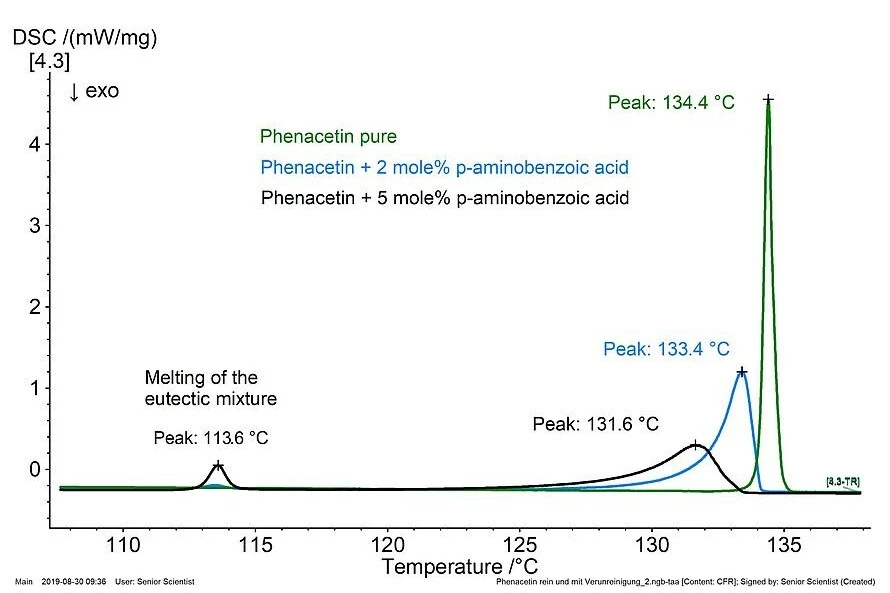
As a result, the melting effect of the major substance broadens and the Melting Temperatures and EnthalpiesThe enthalpy of fusion of a substance, also known as latent heat, is a measure of the energy input, typically heat, which is necessary to convert a substance from solid to liquid state. The melting point of a substance is the temperature at which it changes state from solid (crystalline) to liquid (isotropic melt).melting temperature shifts to lower values (Melting Temperatures and EnthalpiesThe enthalpy of fusion of a substance, also known as latent heat, is a measure of the energy input, typically heat, which is necessary to convert a substance from solid to liquid state. The melting point of a substance is the temperature at which it changes state from solid (crystalline) to liquid (isotropic melt).melting point depression) if an impurity is present. In addition, the melting effect of the eutectic mixture appears.
This relationship is described in ASTM E928, DIN 51 007, USP <891> and Ph. Eur. Chapter 2.2.34.
The purity calculation is done by using the (simplified) Van't Hoff equation.
The graphic shows the alteration of the melting effect of phenacetin as well as the growing melting effect of the eutectic mixture with an increasing amount of the “impurity” p-aminobenzoic acid. Sample masses: 1 - 1.3 mg, heating rate: 1 K/min, N2 atmosphere, Al crucibles.
Other kinds of impurities (non-eutectic ones) can be determined by DSC and/or TGA when an additional effect occurs which is not visible for the pure substance.