Measurement Parameters
TG 209 F1 Libra® - GC-MS
TGA Parameters:
- RT to 500°C
- 10 K/min
- 50 ml/min N2
- Sample mass: 1.71 mg
- Al2O3 crucibles
GC Parameters:
- Quasi-continuous
- GC furnace: 250°C
- Split: 10:1
- Column: HP 5 ms, 30 m
- Valve switching: 30 sec
Introduction
ASA is one of the most widely used non-opioid analgesics. By esterification of the phenolic hydroxyl group of salicylic acid with acetic acid, not only is a better local tolerance achieved, but also a stronger antipyretic, antiphlogistic and especially platelet aggregation inhibiting effect [1].
The common name is 2-acetoxybenzoic acid. It forms white, needle-shaped crystals which smell faintly of acetic acid. ASA is produced by means of the Kolbe-Schmitt synthesis, an electrophilic aromatic substitution [2].
[1] Mutschler, Arzneimittelwirkungen
[2] Laue, Reaktionsmechanismen
Measurement Results
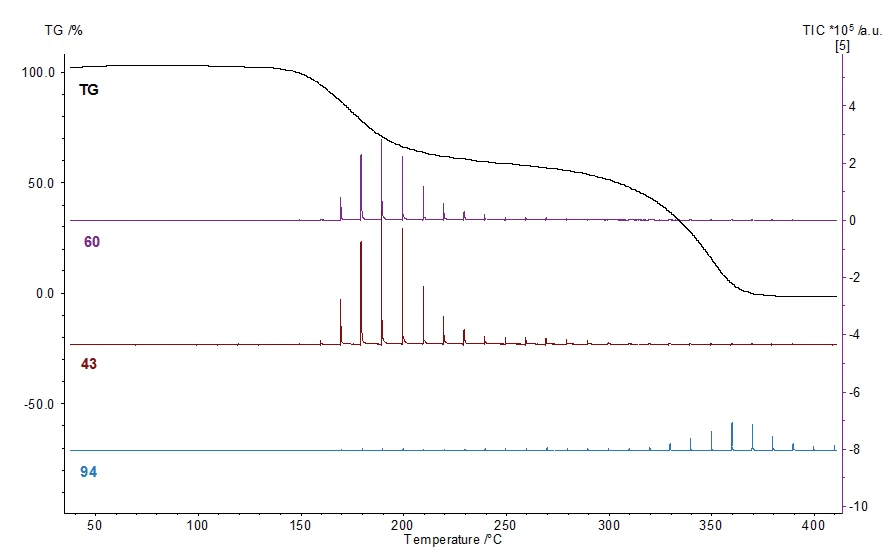
Simultaneous coupling of thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and GC-MS (gas chromatography and mass spectrometry) enables easy analysis of the thermal behavior and Réaction de DécompositionA decomposition reaction is a thermally induced reaction of a chemical compound forming solid and/or gaseous products. decomposition products.
The melting of ASA can be detected by means of c-DTA® at 142°C. ASA decomposes in two steps (DTG minima at 175°C and 350°C). The total ion chromatogram reflects the completely measured spectra as a function of temperature. Corresponding to DTG, two maxima can clearly be seen.
The 1st TG step can be attributed to the formation of acetic acid (mass numbers 43 and 60 figure 4); the 2nd step can be attributed to phenol (mass number 94) as a decomposition product.