Słownik
Sadza
Temperatura i atmosfera (gaz płuczący układ pomiarowy) wpływają w znaczny sposób na wyniki zmiany masy badanej próbki. Zmieniając atmosferę np. z azotu (suchego obojętnego gazu) na powietrze (atmosferę o charakterze utleniającym) podczas pomiaru TGA, możliwe staje się oddzielanie i oznaczanie ilości pewnych dodatków, np. sadzy i polimeru w całkowitej masie próbki.
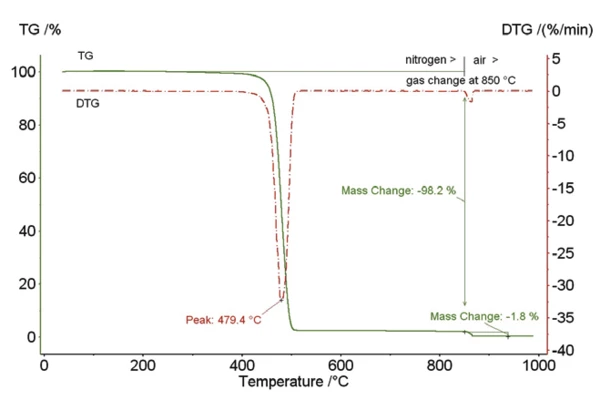

Rysunek 1
Rysunek 1 przedstawia polietylen (PE) wypełniony sadzą w 1,8%. Pierwszy etap rozkładu próbki (pik DTG przy 479°C) dotyczy rozkładu - pirolizy PE. Po przejściu z atmosfery gazu obojętnego (azot) do atmosfery utleniającej (powietrze syntetyczne), sadza dodana w procesie produkcji ulega całkowitemu spaleniu do dwutlenku węgla.
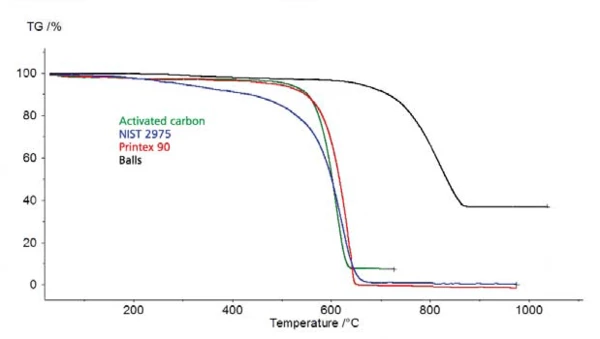
Rysunek 2
The surface of the carbon black determines the combustion behavior (in oxygen atmosphere). The larger the surface area, the smaller the particle size, the lower the combustion temperature or the faster the combustion takes place at a defined temperature (see figure 2).
Due to this combustion behavior, it is in many cases possible to distinguish between added carbon black and Pyrolytic CarbonPyrolytic carbon is carbon which is generated by the pyrolysis of organic matter in an oxygen-free atmosphere. pyrolytic carbon. Therefore, the TGA can be used to determine the carbon black content – even in polymers which form pyrolytic soot.


