applications
Where Can Thermal Analysis and Rheology Be Found in Industry?
From a disease to the pharmaceutical drug product that comes on the market to fight it, the development of new drugs is going through several stages. Methods of thermal analysis accompany and facilitate Research & Development, scale-up and quality control.
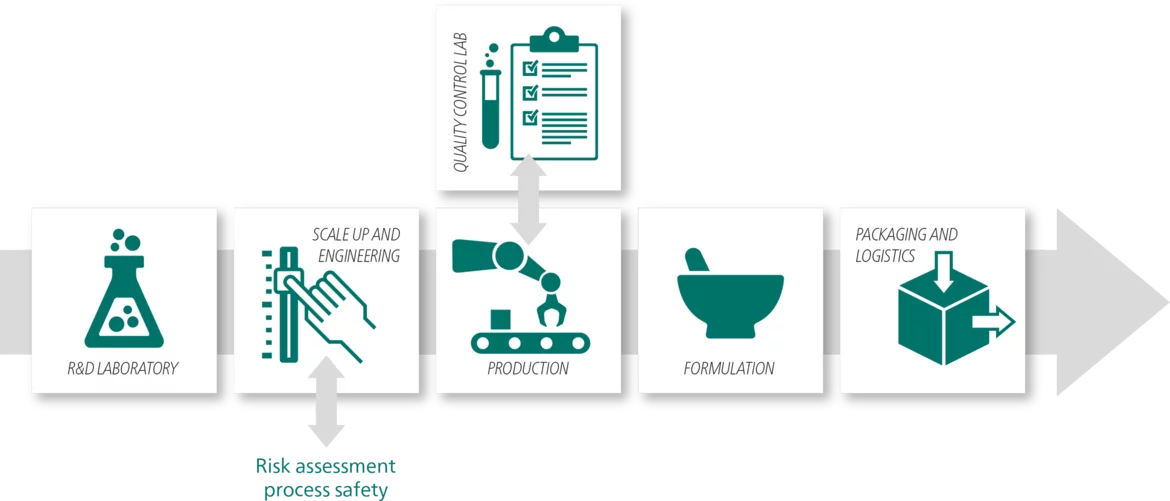

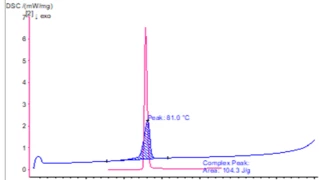
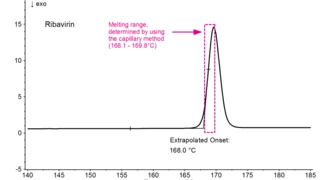
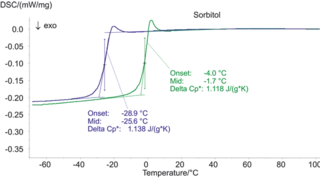
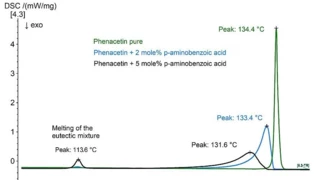
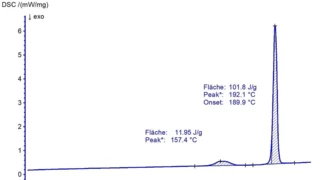
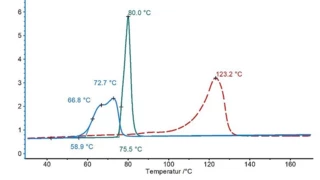
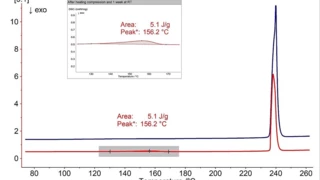
Characterization of the physicochemical properties of a new substance goes hand in hand with pre-formulation and formulation tests. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) is used for the identification of the API or excipient as well as for the determination of their glass transition and/or melting point. If the API exhibits polymorphism, DSC also states the polymorphic modification of the substance. Finally, it gives information about its eutectic purity.
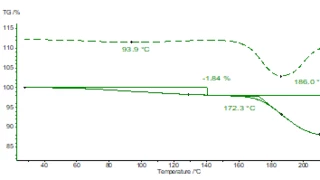
Thermal and oxidative stability are investigated by means of Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA).
Both methods can be used to check the interactions between a pharmaceutical and different excipients and/or packaging materials, giving first information about their compatibility.
Rheometry provides important information, e.g., for appropriate flow properties of sprays and of injectable liquids or for estimating the shelf life of dispersions.

Thermal analysis supports the scale-up from laboratory to the production. DSC and TGA help determine and optimize the process parameters by giving indications about process-induced transformations.
Additionally, NETZSCH offers solutions for continuous and batch mixing, wet and dry micronization and higher-pressure homogenizers (https://www.NETZSCH-grinding.com/en/pharma-cosmetics).
Regarding process safety, DSC and ARC® (Accelerating Rate Calorimetry (ARC)The method describing isothermal and adiabatic test procedures used to detect thermally exothermic decomposition reactions.Accelerating Rate Calorimetry) instruments, often in combination with the Kinetic Neo and Thermal Simulation software packages, can identify chemical hazards and simulate worst-case-scenarios.

Quality control ensures efficacy, safety and quality of commercialized drugs. It concerns the raw materials (active ingredients and excipients), drug delivery systems as well as primary packaging, e.g., blisters or bottles.
DSC and TGA check if a material didn't change its properties during production or if there is a risk of changing its properties during storage and transport (water uptake, polymorphic modification, amorphous/crystalline phase, …); Rheometry takes care of the correct viscosity of semi-solid and liquid drug products – and all that in line with 21 CFR Part 11 (data integrity).